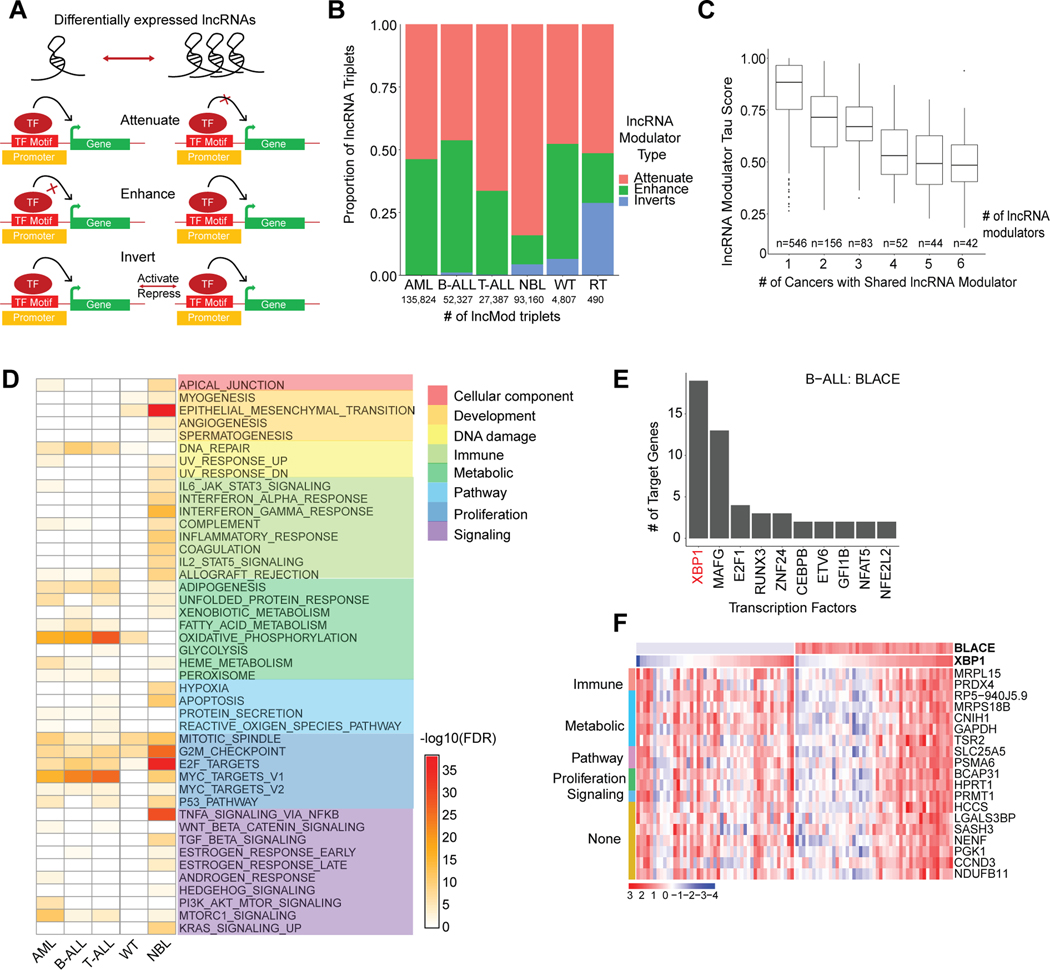
Figure 4: lncRNA modulators impact transcriptional networks involving proliferation.
(A) Schematic that shows the three ways (attenuate, enhance, or invert) in which differentially expressed lncRNA modulators can impact transcription factor and target gene relationships. lncRNA modulators are associated with a TF-target gene pair based on a significant difference between TF-target gene expression correlation in samples with low lncRNA expression (lowest quartile) vs samples with high lncRNA expression (highest quartile). (B) The proportion of lncRNA modulator types associated with significantly dysregulated lncRNA modulator- TF-target gene (lncMod) triplets. The number of significantly dysregulated lncMod triplets is listed per cancer. (C) Number of lncRNA modulators genes that are common in lncMod triplets across cancers. Common lncRNA modulator genes tend to have a lower tau score compared to lncRNA modulators only associated with one cancer. (D) Gene set enrichment using the MSigDB Hallmark gene set, of target genes associated with lncRNA modulators in each cancer (Fisher’s exact test, FDR < 0.1). (E) Transcription factors associated with the B-ALL expression specific lncRNA, BLACE, ranked based on number of regulated target genes. (F) Expression heatmap of BLACE and the target genes of the XBP1 transcription factor, grouped by associated hallmark gene set, in samples within the bottom and top quartiles of BLACE expression in B-ALL.