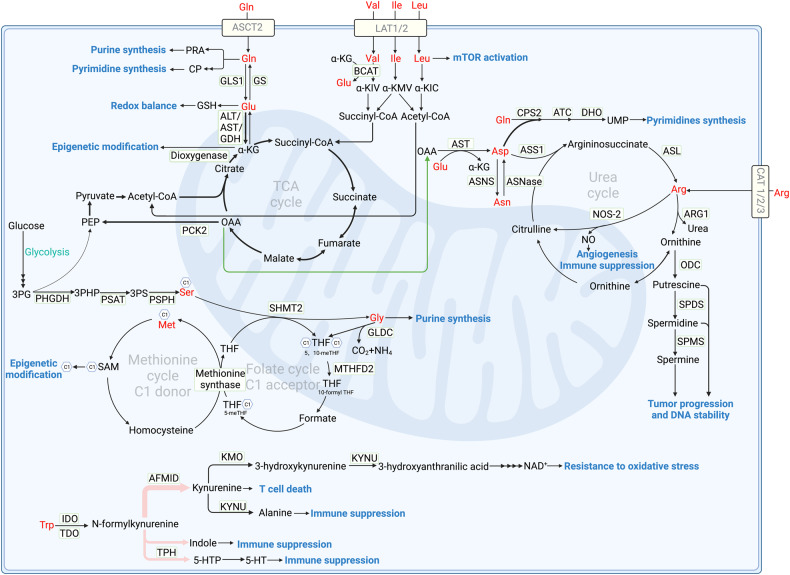
Fig. 1. Amino acid metabolism in tumors.
ASCT2 serves as the primary glutamine transporter, importing glutamine to generate purines and pyrimidines. GLS1 catalyzes glutaminolysis, generating glutamate which synthesizes GSH to maintain redox balance. Glutamate further transfers to α-KG under the catalyze of transaminase or deaminase. Under glucose-limited condition, glutamate derived α-KG acts as an alternative for glucose through participating in TCA cycle. Elevated PCK2 prompts PEP production to fuel TCA cycle. α-KG also act as substrate for DNA dioxygenase in demethylation. LAT1/2 transports BCAAs intracellular, activating mTOR activity and producing BCKA under the catalyze of BCAT2. BCKA can be further catalyzed to acetyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA to fuel TCA cycle. Arginine can be obtained through CAT family transporters, and synthesized de novo under the catalysis of ASS1 and ASL from citrulline in urea cycle. In tumors, ornithine is metabolized by upregulated ODC into polyamines including putrescine, spermidine, and spermine. The overproduction of polyamines results in uncontrolled tumor growth. Besides, NO production under the catalyze of NOS-2 elevates angiogenesis and suppress immune. De novo serine synthesis is catalyzed by PHGDH, PSAT and PSPH. SHMT2 catalyzes glycine and 5,10-methylene-THF production, in which glycine can also be transferred to 5,10-methylene-THF under the catalyze of GLDC, participating in folate cycle and methionine cycle. Besides, glycine also directly supplies carbon for de novo purine biosynthesis. Tryptophan is mainly catalyzed by IDO1 and TDO to produce kynurenine, and finally generates NAD+ and alanine to inhibit immune response and promote cancer progression. Seldom tryptophan metabolizes along the 5-HT and indole pathway, also function to suppress immune response. GLS1 Glutaminase1, GS Glutamine synthetase, GOT Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, GPT Glutamic pyruvic transaminase, GDH Glutamate dehydrogenase, α-KG α-ketoglutarate, OAA Oxaloacetic acid, PCK2 Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase2, PEP Phosphoenolpyruvate, CP Carbamoyl phosphate, PRA Phosphoribosyl amine, ASNS Asparagine synthase, ASNase Asparaginase, CPS carbamoyl phosphate synthase, ATC Aspartate transcarbamylase, DHO Dihydroorotase, ASS1 Argininosuccinate synthase1, ASL Argininosuccinate lyase, ARG1 Arginase1, NOS-2 Nitric oxide synthase-2, ODC Ornithine decarboxylase, SPDS Spermidine synthase, SPMS Spermine synthase, 3PG 3-phosphoglyceric acid, 3PHP 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate, 3PS 3-phosphoserine, PHGDH Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, PSAT Phosphoserine aminotransferase, PSPH Phosphoserine phosphatase, SHMT2 Serine hydroxymethyltransferase2, GLDC Glycine dehydrogenase, MTHFD2 Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase2, THF Tetrahydrofolate, SAM S-adenosyl methionine, IDO Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, TDO Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase, AFMID arylformamidase, KMO Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase, KYNU Kynureninase, TPH Tryptophan hydroxylase, Gln Glutamine, Glu Glutamate, Val Valine, Ile Ileucine, Leu Leucine, Asp Asparate, Asn Asparagine, Arg Arginine, Ser Serine, Gly Glycine, Met Methionine, Trp Tryptophan.