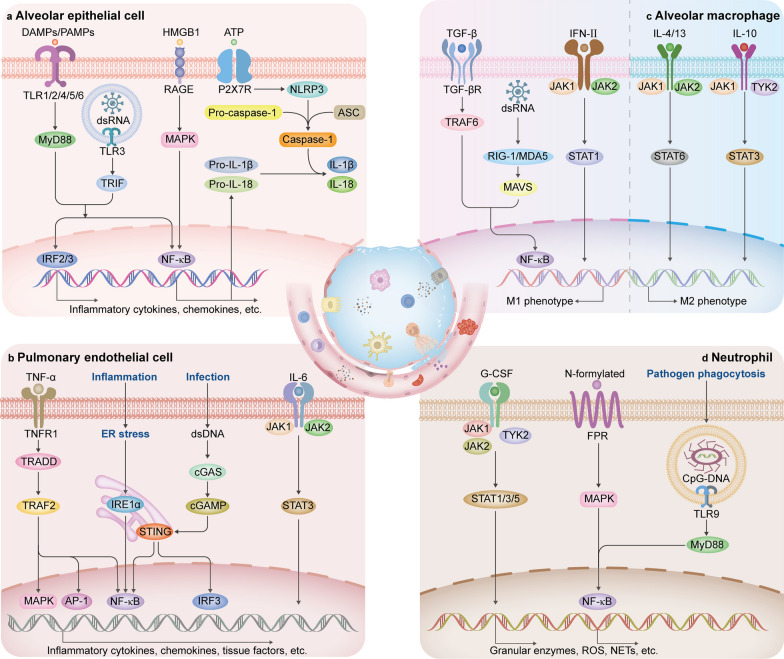
Fig. 2.
Inflammatory signaling pathways activated in AECs, pulmonary endothelial cells, AMs and neutrophils during ARDS. a Signaling pathways in AEC activation, leading to an increase of inflammation. b Signaling pathways in pulmonary endothelial cells, promoting inflammation and coagulation. c Signaling pathways in the regulation of macrophage polarization. The left area of the dashed line promotes AM to exhibit M1 phenotype, while the right area of the dashed line promotes M2 polarization. d Signaling pathways in neutrophil activation. AP-1, activator protein-1; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; cGAMP, cyclic dinucleotide cyclic GMP-AMP; cGAS, cyclic GMP-AMP synthase; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; FPR, N-formyl peptide receptor; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; HMGB1, high-mobility group box 1; IRE1α, inositol requiring kinase 1α; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; JAK, janus kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat protein 3; P2X7R, P2X7 receptor; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; RAGE, receptor for advanced glycation end product; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible gene I; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; STING, stimulator of interferon gene; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TGF-βR, transforming growth factor-β receptor; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNFR1, TNF receptor 1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; TRADD, TNFR-associated death domain; TRAF, TNFR–associated factor; TRIF, Toll/interleukin-1 receptor-domain-containing adaptor-inducing interferon-β; TYK2, tyrosine kinase 2; IFN, interferon