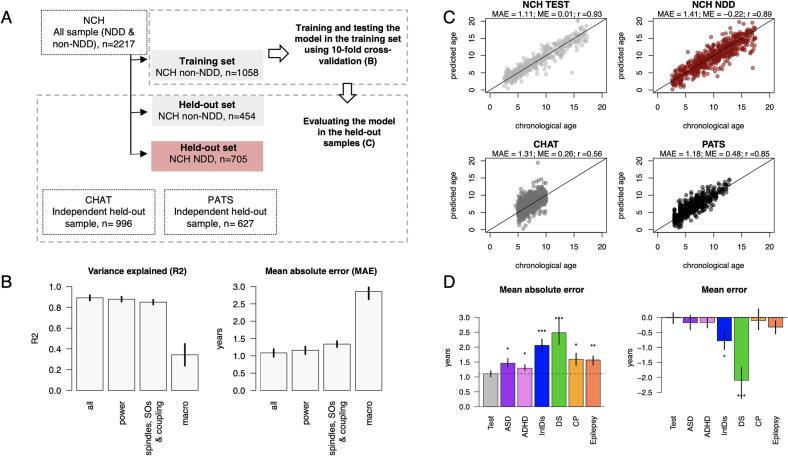
Fig. 5.
Brain age prediction based on sleep micro- and macro-architecture in non-NDD and NDD samples. A – a schematic illustration of the samples and steps used to predict individual chronological age based on sleep features. B – model performance based on different domains of sleep features using 10-fold cross validation. Metrics plotted are the explained variance and mean absolute error (the error bars represent SD across folds). C – The scatterplots show predicted vs true chronological age for all held-out datasets with mean absolute error (MAE), mean error (ME) and Pearson’s correlation (r) between chronological and predicted age reported for each sample. D – Bar plots illustrate MAE and ME for each NDD subgroup in comparison to the non-NDD held-out sample. We estimated variability of these estimates by repeating the analysis 100 times where NCH non-NDD training and non-NDD held-out set were resampled each round, but the disorder subgroups remained unchanged. The resulting 100 estimates of MAE and ME were averaged and illustrated in bar plots (error bars are min and max values across 100 rounds). Stars indicate statistical difference between estimates in each clinical subgroup vs testing set (* - p < 0.05, ** - p < 0.01, *** - p < 0.0 01).