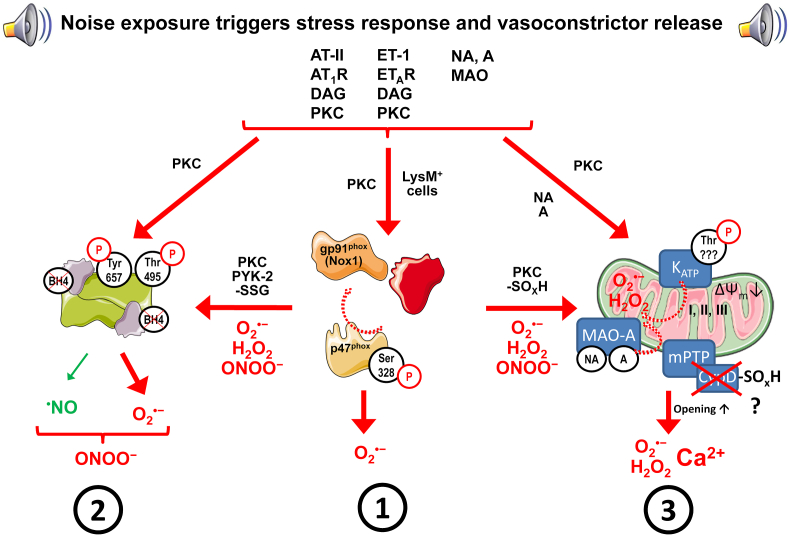
Fig. 14.
Oxidative stress pathways activated by noise. Noise causes stress hormone release (catecholamines and cortisol) and downstream endocrinal activation of vasoconstrictors activating common disease pathways, such as oxidative stress. Angiotensin II (AT-II) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) lead to the formation of diacylglycerol (DAG), a potent activator of protein kinase C (PKC), via their receptors. (1) PKC via phosphorylation of p47phox at serine 328 causes activation of the phagocytic NADPH oxidase (NOX-2) and potentially NOX-1. The expression of NOX-2 is upregulated by noise-triggered immune cell infiltration (lysozyme M-positive (LysM+) cells) and systemic inflammatory conditions. NOX-2 (and NOX-1, especially in the brain) produces superoxide (O2•−) and via dismutation also hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). NOX-4 was not changed by noise and NOX-5 (relevant for humans) was not studied so far. (2) Dysfunction of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) is mediated by noise-dependent activation of PKC and phosphorylation of threonine 495. Alternatively, NOX-2-dependent ROS formation may activate PKC [349] and protein tyrosine kinase 2 (PYK-2) [350,351], causing adverse phosphorylation at tyrosine 657 and threonine 495. Uncoupling of eNOS may be induced by noise-driven oxidative depletion of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) and S-glutathionylation (-SSG) of eNOS by ROS originating from NOX-2 [352]. Semi-uncoupled eNOS may represent a potent source of peroxynitrite. (3) Noise also leads to mitochondrial ROS formation, generating both O2•− and H2O2. Noradrenaline (NA) and adrenaline (A) originating from sympathetic activation are substrates of monoamine oxidases (MAO) that produce H2O2. PKC seems to activate the mitochondrial KATP channel by phosphorylation of a threonine residue with subsequent depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane (ΔΨm↓) and O2•− formation from respiratory complexes I, II and III. Mitochondrial H2O2/O2•− and calcium are released to the cytosol upon the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening (e.g., by thiol oxidation of the regulatory subunit cyclophilin D (CypD) [353]). KATP channel activation and mPTP opening can also be stimulated by redox-crosstalk with H2O2 (probably also O2•− via peroxynitrite) derived from NOX-2 [197]. So far, there is no evidence for the role of xanthine oxidase in noise's non-auditory (indirect) effects. This scheme contains images from Servier Medical Art by Servier, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License.