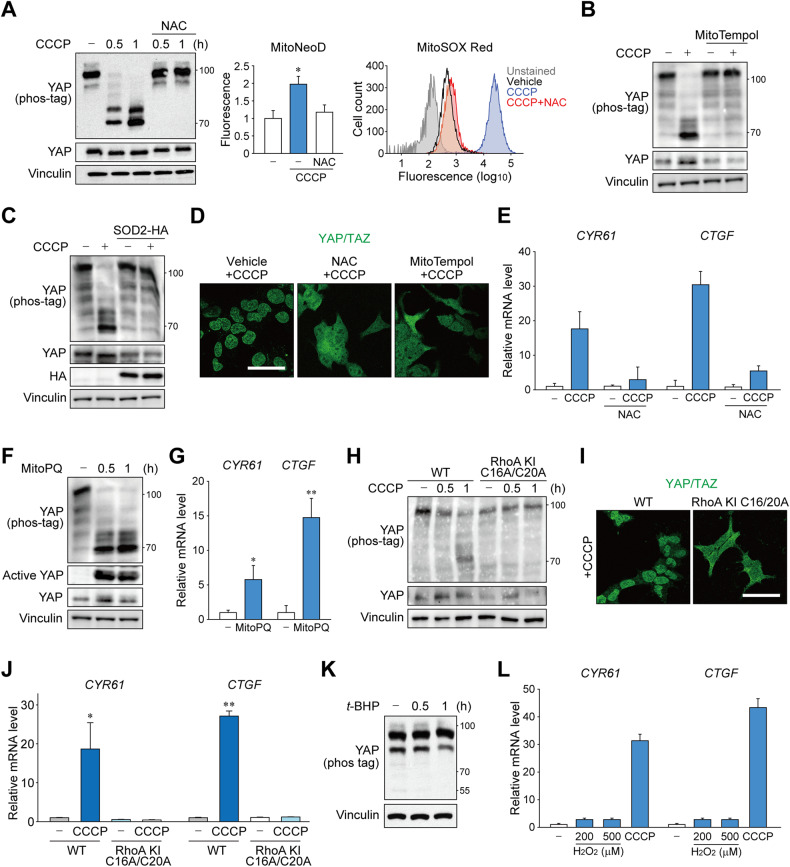
Fig. 4. Mitochondrial superoxide triggers RhoA activation for YAP dephosphorylation.
A Mitochondrial superoxide is essential for CCCP-induced YAP activation. Cells were pretreated with 2 mM N-acetylcysteine (NAC) before CCCP (1 h) treatment and analyzed by immunoblotting (left), fluorometry after staining with 5 μM MitoNeoD (middle), or flow cytometry after labeling with 2 μM MitoSOX Red (right). B Cells were treated with CCCP (1 h) after mitoTempol (100 μM, 1 h) or vehicle pretreatment, then danalyzed using Phos-tag immunoblot. C Phos-tag and regular immunoblots for YAP. Cells were transfected with HA-tagged SOD2 expression vector and treated with CCCP (1 h) after 24 h. D Superoxide scavengers impede YAP/TAZ nuclear localization. Cells were treated with CCCP (1 h) after NAC (2 mM), mitoTempol (100 μM) or vehicle treatment, then used for YAP/TAZ immunostaining. Scale bar: 50 μm. E qRT-PCR for YAP/TAZ target genes. Cells were treated with CCCP (1 h) after NAC (2 mM) or vehicle treatment. F, G Phos-tag and regular immunoblots (F) and qRT-PCR of target genes for YAP activity assay. Cells were treated with mitoPQ (10 μM) for indicated times or 3 h, respectively. H–J Cells with superoxide-irresponsible mutant RhoA does not induce YAP activation. YAP phosphorylation was compared in wild-type cells or cells with C16A/C20A knock-in mutation on endogenous RhoA. H Phos-tag immunoblots for YAP using cells treated with CCCP for indicated times. I Immunostaining for YAP/TAZ after CCCP for 3 h. J RT-qPCR analysis for YAP target genes after treatment with CCCP for 3 h. K tert-butylhydroperoxide (t-BHP; 500 μM) were given to cells for indicated times and analyzed using Phos-tag immunoblotting for YAP. (L) Cells were treated with increasing concentrations of hydrogen peroxide as indicated or CCCP for 3 h and analyzed by qRT-PCR. For A–L, HEK293 cells were serum-starved for 12 h to 16 h prior to CCCP (50 μM) treatment.