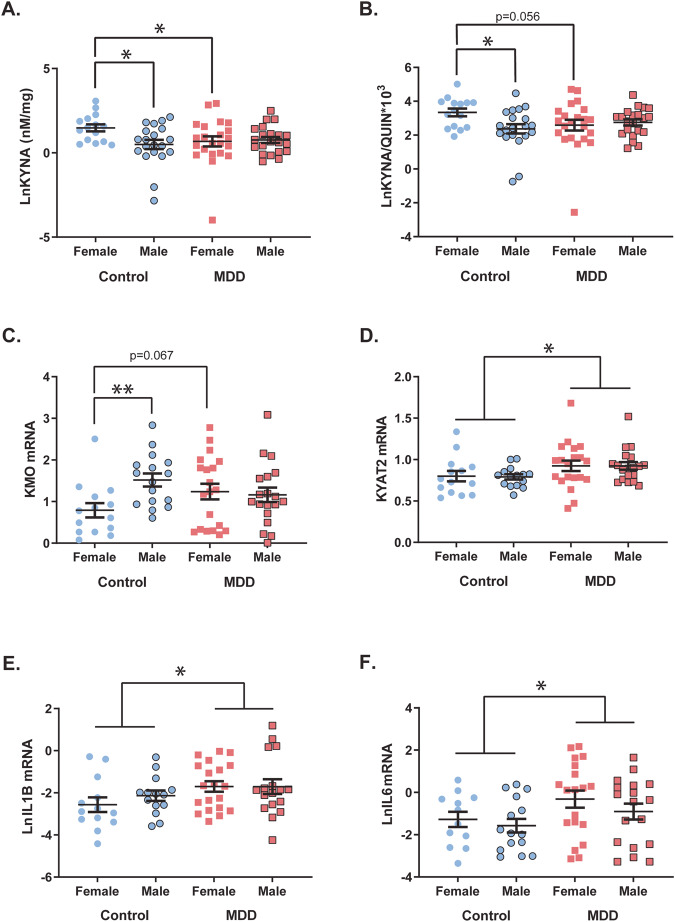
Fig. 1. Sex-specific alterations in the kynurenine pathway are present in major depressive disorder.
A Kynurenic acid (KYNA) was significantly decreased in females with major depressive disorder (MDD) compared to controls (p = 0.036). KYNA was significantly higher in female controls compared to male controls (p = 0.012). B The KYNA/QUIN ratio was significantly higher in female controls compared to male controls (p = 0.017). There was a trend decrease in the KYNA/QUIN ratio in females with MDD compared to female controls (p = 0.056). C KMO mRNA was significantly higher in male controls compared to female controls (p = 0.004). In females, MDD subjects had a trend increase in KMO mRNA compared to female controls (p = 0.067). D There was a main diagnostic effect for KYAT2 mRNA. KYAT2 mRNA was significantly increased in MDD compared to controls (p = 0.025). E IL1B and (F) IL6 mRNAs were significantly increased in MDD compared to controls (p = 0.017, p = 0.039, respectively). Controls are represented by circles and MDD subjects are represented by squares. Outlined shapes represent male subjects. Bars indicate mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.