Fig. 11. The proposed interaction between IND and LPAR2.
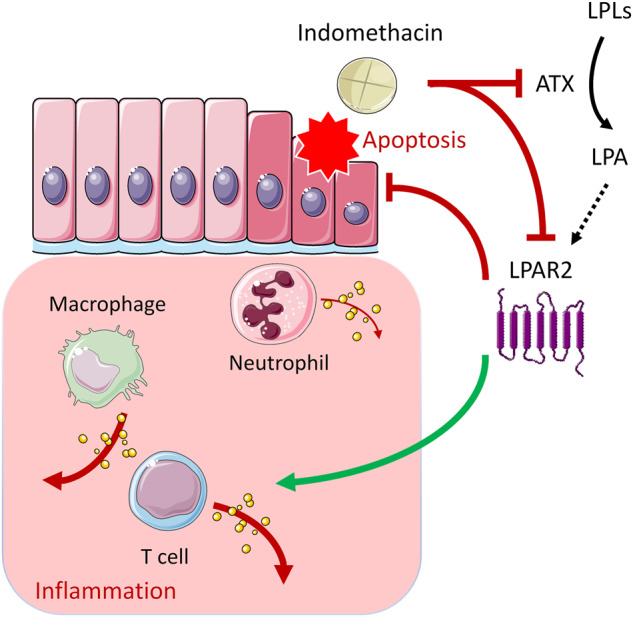
IND treatment inhibits the plasma activity of autotaxin (ATX), and also downregulates the intestinal expression of LPAR2. LPAR2 exerts dual effect on IND-induced enteropathy; it mitigates the severity of mucosal damage, at least partly due to inhibition of intestinal apoptosis, but also potentiates the inflammatory reaction associated with ulceration. This latter effect involves the increased activation of several immune cells, including T cells, but not that of neutrophils, whose number and activity rather change in parallel with the severity of mucosal damage. LPLs: lysophospholipids.
