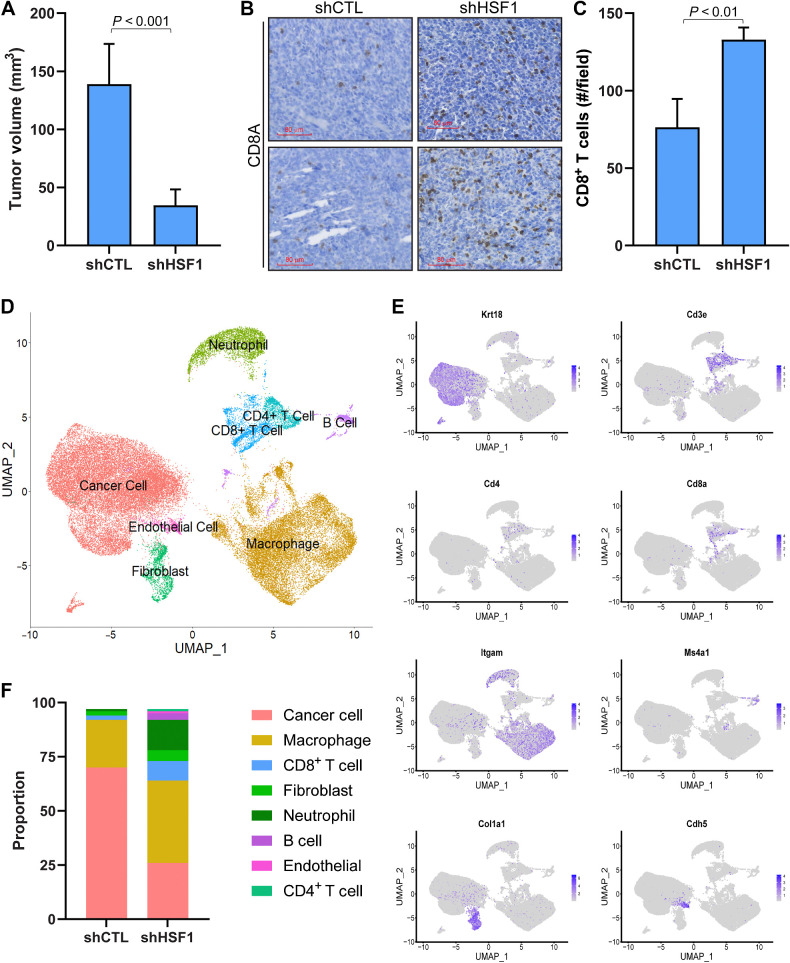
Figure 6.
HSF1 Functionally regulates the amount of CD8+ T cells in breast tumors. A, 4T1 cells (5 × 104 cells) with (n = 5) or without (n = 5) HSF1 knockdown were grown orthotopically in Balb/c mice for 3 weeks. Tumor volume at the conclusion of the study is graphed. B, IHC was performed on tumors from A detecting CD8A to identify CD8+ T cells. C, CD8+ T cells from B were quantified for control and HSF1 knockdown tumors by manual counting positive cells in >5 fields of the tumor tissue area. D–F, shCTL and shHSF1 tumors from A were subjected to scRNA-seq. Processed reads were used to map cell clusters for both samples using Seurat 4.2.0. The Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) integrating both samples is shown in D. These cell types were annotated using expression of specific marker genes for each population, for which a sample of these marker genes is shown in E. The proportion of each cell population was also calculated and graphed in F.