FIGURE 4.
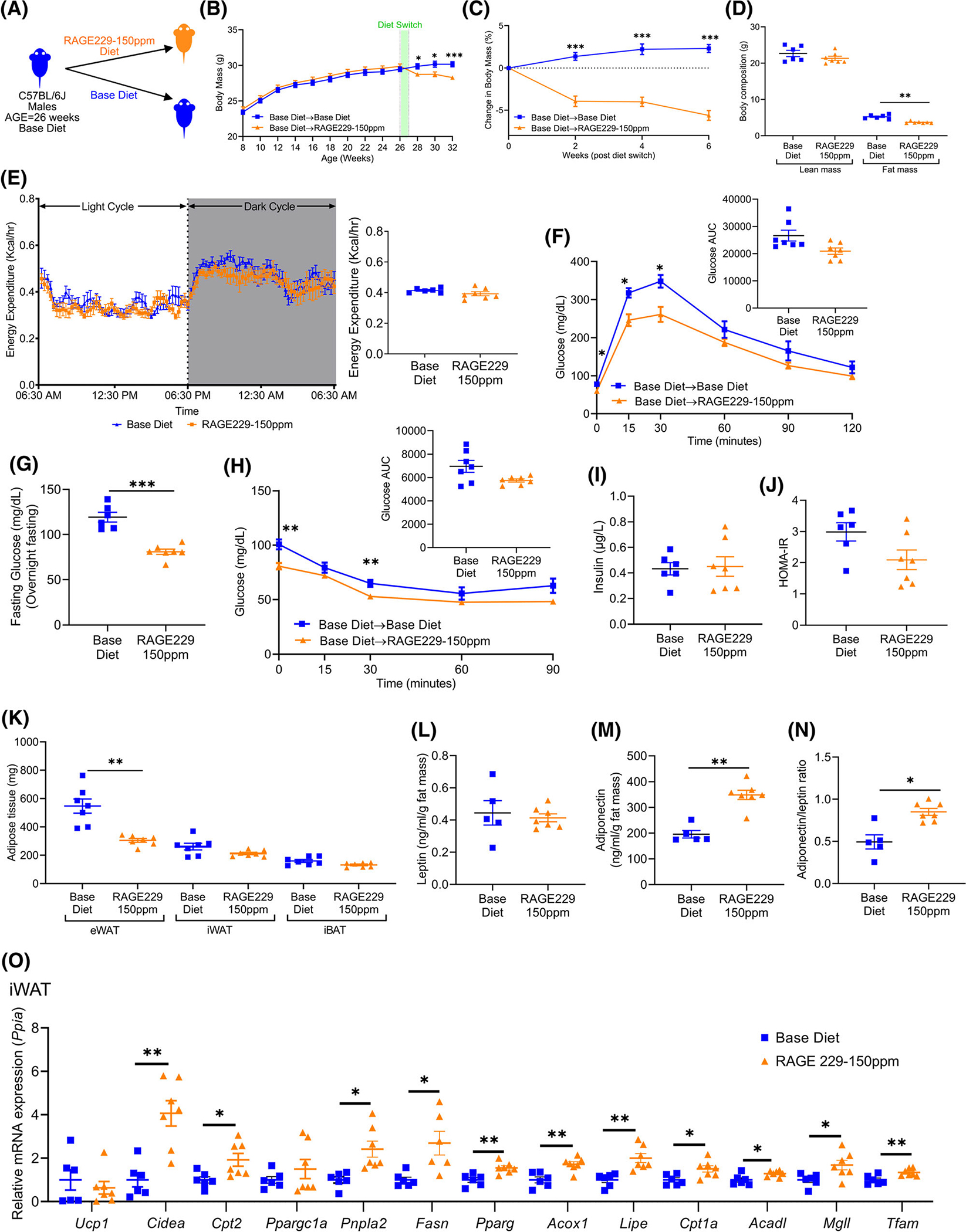
Administration of RAGE229–150 ppm diet to lean male mice causes loss of body and fat mass and improves metabolic health. (A) Experimental schematic. (B) Body mass recorded over the indicated time course in mice fed base diet until age 26 weeks; mice then remained on base diet (n = 24) or were switched to RAGE229–150 ppm diet (n = 27). (C) Change in body mass (%) over 6 weeks after diet switch. (D) Lean mass and fat mass measured at 9 weeks after diet switch by DXA (n = 6 base diet, n = 7 RAGE229 diet). (E) Energy expenditure (light and dark cycle) measured at 10 weeks after diet switch (n = 6 base diet, n = 7 RAGE229–150 ppm diet). (F) Post-overnight fasting glucose tolerance test at 6 weeks after diet switch (n = 7 per group). (G) Post-overnight fasting plasma glucose at 12 weeks after diet switch (n = 6 base diet, n = 7 RAGE229–150 ppm diet). (H) Post-6-hour fasting insulin tolerance test at 7 weeks after diet switch (n = 7 per group). (I,J) Post-overnight fasting plasma insulin and HOMA-IR at 12 weeks after diet switch (n = 6 base diet, n = 7 RAGE229–150 ppm diet). (K) Adipose tissue depot mass collected from randomly fed mice 12 weeks after diet switch (n = 7 per group). (L–N) Post-overnight fasting plasma leptin/fat mass, adiponectin/fat mass, and adiponectin/leptin ratio at 12 weeks after diet switch (n = 5 base diet, n = 7 RAGE229–150 ppm diet). (O) Relative expression of the indicated metabolic and thermogenic genes in iWAT collected from randomly fed mice (n = 6 base diet, n = 6–7 RAGE229–150 ppm diet) at 6 weeks after diet switch. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Data presented in panels B and C are combined from four independent cohorts. Multiple cohorts were employed for replication and in order to execute all of the biochemical, molecular, and physiological studies reported in this figure. For analysis of absolute body mass (panel B) over the indicated time period, piecewise linear mixed-effect model was fitted with node set at 26 weeks and difference was tested between the body mass of base diet and RAGE229–150 ppm diet groups after diet switch. A linear mixed-effect model was adopted for correlated/time-series data (B,C,E,F,H) with post hoc t test for group comparisons at each time point. For group comparison, the Shapiro–Wilk normality test was conducted first for each group with prespecified significance level of 0.1, and if passed, the t test was implemented whereas the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test/Wilcoxon rank sum test was used if normality was not established. AUC, area under the curve; DXA, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance; eWAT, epididymal white adipose tissue; iBAT, interscapular brown adipose tissue; iWAT, inguinal white adipose tissue; RAGE229, receptor for advanced glycation end products. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
