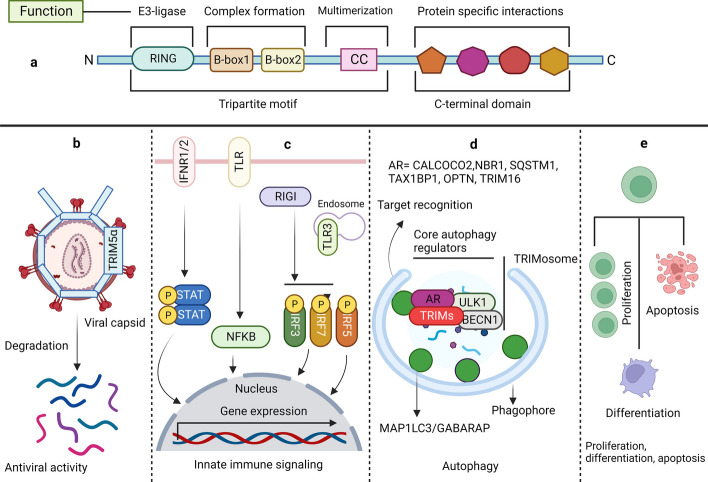
Fig. 1.
TRIM proteins possess a unique RBCC domain at their N-terminus and regulate various biological processes. a Domain organization of TRIM proteins at the N- and C-termini. The N-terminus contains a conserved RBCC domain, whereas the C-terminus contains variable domains required for protein‒protein interactions and substrate selection. b TRIM5α provides immunity against retroviruses, including HIV-1. It forms a hexagonal ring around the capsid, preventing the release of the genome and targeting the autophagosome-mediated degradation of HIV-1. c TRIM proteins regulate signaling events emanating from IFN receptors, TLRs, and RIGI receptors and activate IFN and NFKB signaling to produce proinflammatory cytokines. d TRIMs interact with the core components of autophagy, such as the BECN1-ULK1 autophagy-initiating complex and Ub-interacting autophagy receptors, to efficiently target substrates to autophagosomes for lysosome-mediated degradation. e TRIM proteins are essential regulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. TRIM; Tripartite motif containing, RBCC; RING, B-box, Coiled-coil, TRIM5α; Tripartite motif containing 5α, HIV-1, Human immune deficiency virus-1, IFN; Interferon, TLR; Toll-like receptor, TLR3; Toll-like receptor 3, RIGI; RNA sensor RIG-I, NFKB; Nuclear factor kappa B, BECN1; Beclin 1, ULK1; Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1, TLR3; Toll-like receptor 3, RING; Really interesting new gene, IFNR; Interferon production regulator, IRF3; Interferon regulatory factor 3, IRF5; Interferon regulatory factor 5, IRF7; Interferon regulatory factor 7, AR; Autophagy receptor, CALCOCO2; Calcium binding and coiled-coil domain 2, NBR1; NBR1 autophagy cargo receptor, SQSTM1; Sequestome 1, TAX1BP1; Tax1 binding protein 1, OPTN; Optineurin, TRIM16; Tripartite motif containing 16, MAP1LC3; Microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3, GABARAP; GABA type A receptor-associated protein, STAT; Signal transducer and activator of transcription