Fig 2.
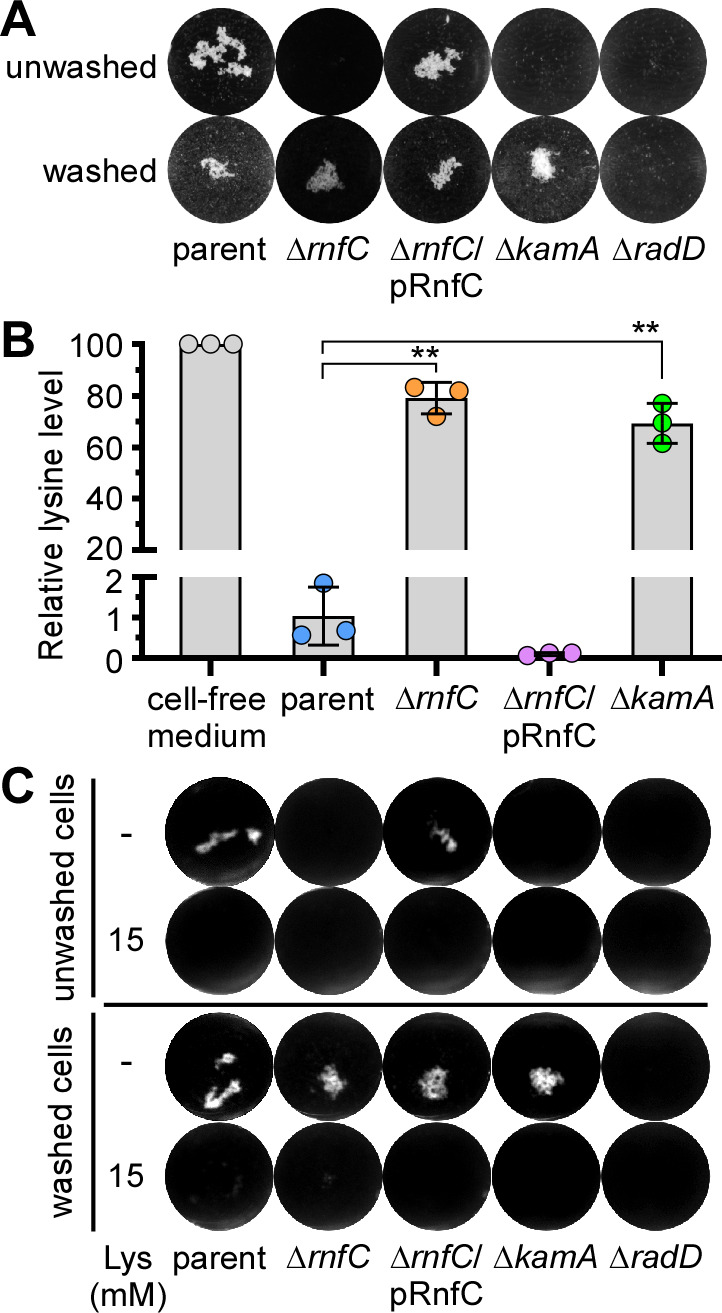
A non-polar, in-frame rnfC deletion mutant is defective in RadD-mediated coaggregation and lysine uptake. (A) The parent, rnfC deletion mutant, and rnfC-complemented strains were tested for their ability to co-aggregate with S. gordonii. Fusobacterial cells were washed or unwashed before being mixed in equal volumes with washed S. gordonii and imaged. Mutants devoid of radD or kamA, a lysine metabolic pathway gene (24), were used as references. (B) The relative level of lysine in the cell-free culture medium of indicated strains grown to stationary phase was determined by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, with the level of lysine in media without bacteria set to 100. (C) The same coaggregation experiment as (A) was performed with or without addition of 15 mM lysine. All results were obtained from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Significance was calculated by a Student’s t-test; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
