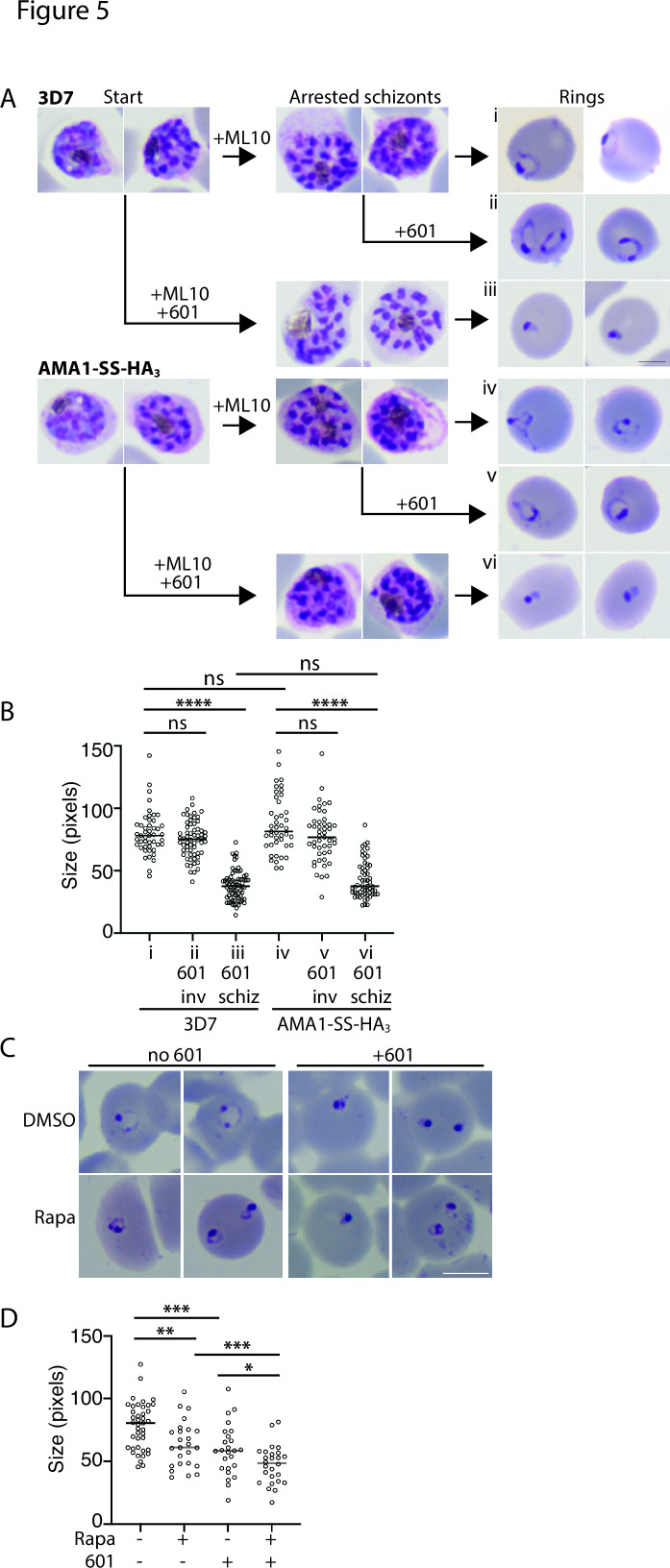
Fig 5.
Developmental arrest induced by Plasmepsin V inhibitors after invasion. (A) Synchronized cultures of 3D7 and AMA1-SS-HA3-PV6 parasites were treated with ML10 when the parasites were in the early schizont stage, and half of the culture was simultaneously treated with the PM V inhibitor WEHI-1252601 (601) (Start). ML10 and 601 were removed when most schizonts appeared arrested (Arrested schizonts). The culture treated only with ML10 was split into two, and one half was treated with 601. Ring formation was determined 1 h after the removal of ML10 (Rings). The scale bar on the right-hand side of panel iii represents 2.5 µm. (B) Quantitation of parasite diameter size in samples i–vi in panel A. Indicated is the time the PM V inhibitor 601 was added; inv, after removal of ML10 from arrested schizonts; schiz, at start in Panel A (and removed with ML10). Data are based on the measurement of at least 40 rings. The Mann–Whitney U test was performed for statistical analysis; ns: not significant, ****P < 0.0001. (C) Treatment of parasites containing a floxed pv6 locus with rapamycin and 601, as indicated. Note the more compact shape of the parasites treated with 601 compared to the rapamycin-treated parasites. The scale bar represents 5 µm. (D) Quantitation of parasite sizes from the experiment shown in panel C. Data are based on the measurement of at least 20 rings. The Mann–Whitney U test was performed for statistical analysis: ns: not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.