Figure 6.
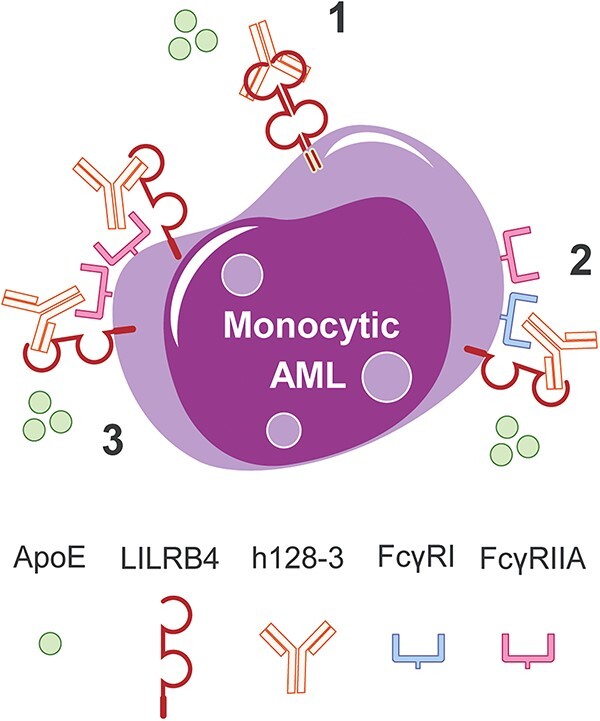
FcγR-dependent and independent mechanisms of h128-3-induced LILRB4 internalization on monocytic AML. Depending on the monocytic AML cell surface levels of functional FcγRs, h128-3 binds and internalizes its LILRB4 target receptor on these malignant cells by three potential mechanisms: (1) on all monocytic AML cells, h128-3 crosslinking of LILRB4 receptors triggers clathrin-mediated endocytosis and lysosomal receptor degradation; (2) on FcγRhigh monocytic AML cells, high-affinity FcγRI scaffolds h128-3 to target LILRB4, leading to internalization and degradation; and (3) on FcγRI−FcγRIIA+ monocytic AML cells, low-affinity FcγRIIA scaffolds h128-3 by avidity to target LILRB4, prompting its internalization and degradation.
