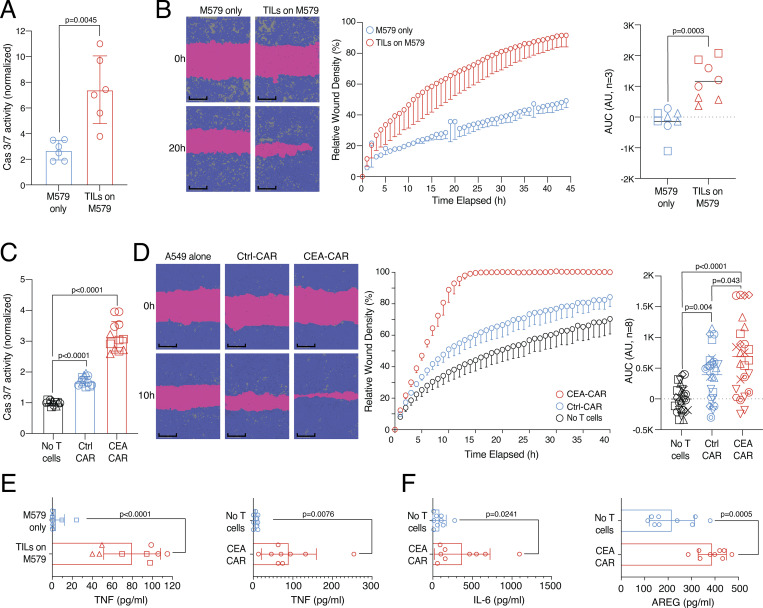
Figure 5.
Human CD8 TILs and CAR T cells can support tumor cell killing and wound healing in vitro. (A) TIL-target cell coculture with killing activity of TILs measured via green fluorescence (Cas 3/7, n = 3, unpaired t test). (B) Wound healing assay with HaCaT cells using SN derived from TIL-target cell coculture or M579 only. Statistical verification across experiments using background-subtracted AUC (n = 3, unpaired t test of AUC, symbols indicate individual experiments). Scale bars = 400 µm; enhanced for improved visibility. (C) CEA-CAR-transgenic CD8 T cells, Ctrl-CAR-transgenic CD8 T cells, or no T cells were cocultured with CEA-expressing A549 target cells. Killing activity of CAR T cells was measured via green fluorescence (Cas 3/7, n = 3, unpaired t test, symbols indicate individual experiments). (D) Wound healing assay with SN derived from CEA-CAR-transgenic CD8 T cells versus Ctrl-CAR-transgenic CD8 T cells or no T cells. Representative example; more donors in Fig. S4. Statistical verification across experiments using background-subtracted AUC (n = 8, one-way ANOVA of AUC, symbols indicate individual experiments). Scale bars = 400 µm; enhanced for improved visibility. (E) TNF in TIL-target cell co-culture (left, n = 3, unpaired t test, symbols indicate individual experiments) or CEA-CAR-transgenic CD8 T cell coculture (right, n = 9, paired t test). (F) IL-6 (left) and AREG (right) in CEA-CAR-transgenic CD8 T cell co-culture (n = 9, paired t test). All data were derived from two or more independent experiments with the indicated number of replicates.