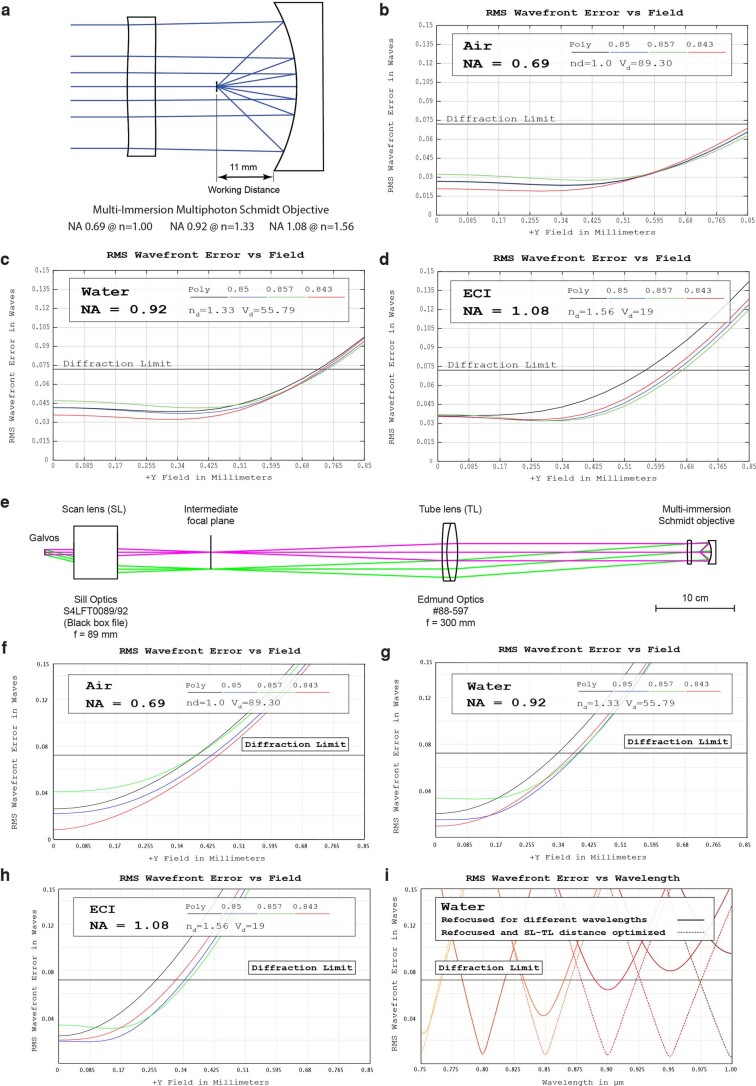
Extended Data Fig. 1. Theoretical performance of the Schmidt objective and the microscope.
a) Cross-section of the optical design. b)–d) Root-mean-square (RMS) wavefront aberration vs. FOV of the objective in air, water, ECI, respectively. e) Cross-section of the laser-scanning path. f)–h) Root-mean-square (RMS) wavefront aberration vs. FOV of the objective in air plus scan path, water, ECI, respectively. Due to off-axis aberrations, the usable diffraction-limited FOV is reduced compared to the objective as a stand-alone item. i) On-axis RMS wavefront aberrations vs. wavelength. The system can be refocused to different wavelengths in the 750-1000 nm region. For best results, both the mirror-correction plate distance and the spacing of scan and tube lens can be optimized.