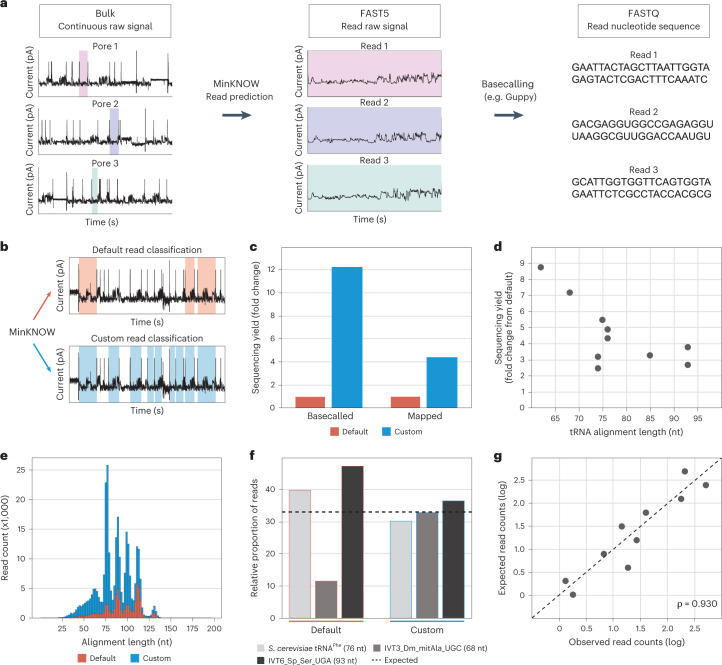
Fig. 3. Adjustment of MinKNOW parameters increases the number of sequenced and mapped tRNA reads.
a, MinKNOW software classifies continuous current passing through pores as open pore, adapter or strand (actual reads) and outputs fragments classified as strand to a FAST5 file, which are then basecalled to generate a FASTQ file. b, Diagram showing the conceptual difference between default and custom MinKNOW read classification (Extended Data Fig. 4). c, Bar plot of sequencing yield in terms of basecalled and uniquely mapped reads obtained with default and custom configurations (Supplementary Table 7). d, Scatter plot of the relative fold change of uniquely mapped reads with respect to tRNA length (Supplementary Table 8). e, Histogram of read count and alignment length of IVT tRNA reads captured with default and custom configurations. f, Bar plot of the relative proportion of IVT tRNA molecules D. melanogaster mitochondrial tRNAAla(UGC) and S. pneumoniae tRNASer(UGA) and native S. cerevisiae tRNAPhe reads recovered with default and custom settings (Supplementary Table 9), where the dotted line indicates the expected proportion. g, Expected versus observed log read counts of nine IVT and one native tRNA molecules captured using the custom MinKNOW configuration (Supplementary Table 10). Spearman correlation (ρ) is shown.