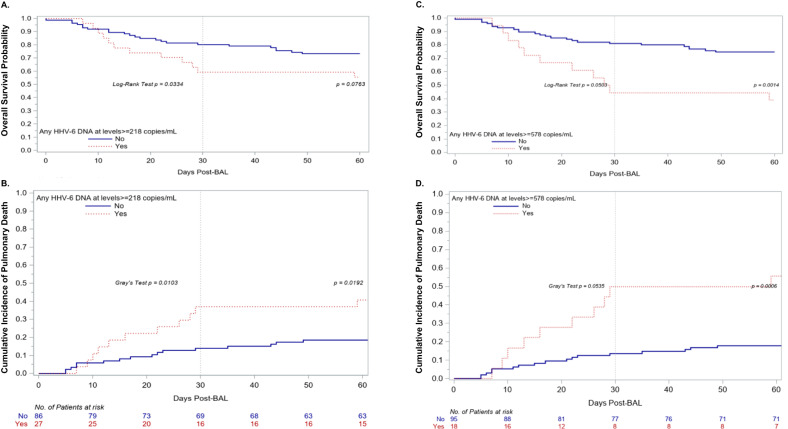
Fig. 3. Kaplan–Meier and cumulative incidence plots of time to overall mortality and death due to respiratory failure, respectively, among patients with and without HHV-6B detection in the BAL at different viral load thresholds.
Participants with HHV-6B DNA ≥ 218 copies/ml (2.3 log10 copies/mL) in BALF based on the threshold predictive of detection of at least one of two mRNA transcripts (n = 27) had increased overall mortality (A) and death from respiratory failure (B). Participants with HHV-6B DNA ≥ 578 copies/ml (2.8 log10 copies/mL) in BALF based on the threshold predictive of detection of both mRNA transcripts (n = 18) had a greater increased risk for overall mortality (C) and death from respiratory failure (D). Deaths due to other causes were considered competing events in the cumulative incidence curves. The first and second log-rank or Gray’s test statistics in the figures depict the unadjusted comparison of the curves at day 30 and day 60 post-BAL, respectively, and were two-sided. Results from adjusted Cox regression models are detailed in Tables S4–S5.