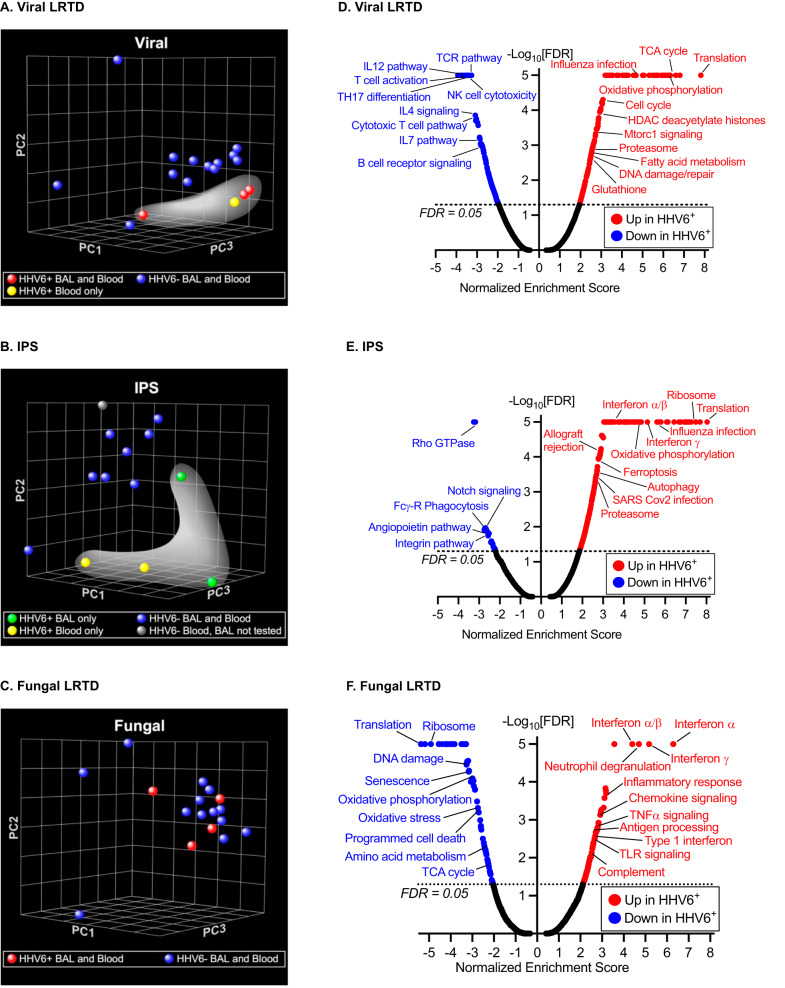
Fig. 4. Genome-wide host expression profiling distinguishes between patients with and without HHV-6B detection.
Panels (A–C) depict multidimensional scaling using principal components analysis (PCA) of the entire transcriptome from whole blood to compare between participants with and without HHV-6B detection, among those with a specific clinically determined LRTD diagnosis. Among 17 participants with a viral pneumonia, PCA analysis suggested segregation between those with HHV-6B detection in the BAL and/or plasma (white highlight) versus those without (A). Among 13 participants with IPS, PCA analysis also suggested segregation between those with HHV-6B detection in the BAL and/or plasma (white highlight) versus those without (B). No clear pattern was seen among 17 participants with fungal pneumonia (C). Panels (D–F) display volcano plots of results from pathway analysis using Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) to define and compare transcriptional programs by HHV-6B detection status in the same subgroups as panels (A–C). Each plot depicts gene sets that are either significantly upregulated (to the right of the plot) or downregulated (to the left of the plot) in participants with HHV-6B detection in BALF and/or plasma compared to those without. A false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 was used to designate significant enrichment of gene sets. Note: Only one patient in the bacterial subgroup had HHV-6B detection in the BAL or plasma, so this group was not further analyzed.