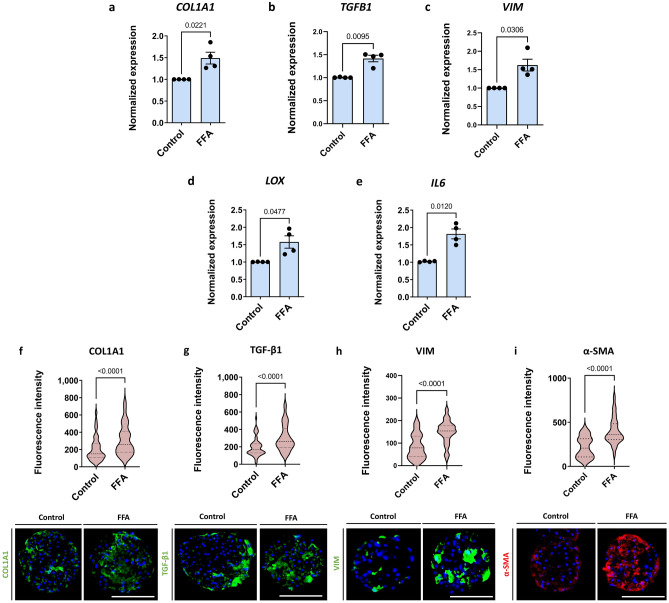
Figure 2.
3D human liver spheroids comprised of hepatocytes and non-parenchymal liver cells can mimic the pathology of hepatic fibrosis. To assess the propensity of the system to develop liver fibrosis-like features, the spheroids were treated with FFA for 7 days. (a–e) Fibrosis-related genes COL1A1, TGFB1, VIM, LOX, and IL6 were upregulated upon FFA treatment (n = 4). (f–i) Representative images of COL1A1, TGF-β1, vimentin, and α-SMA deposition in the control or FFA-treated spheroids show an increase following a 7-day treatment with FFA (n = 4). Blue bars represent mRNA expression data. Data is shown as mean ± SEM. Red violin plots show results of IHC analysis, where plots are created based on the fluorescence intensity (integrated density of the corresponding channel divided by the area of DAPI staining) of 10–20 sections of different spheroids per experiment. The number of experiments included in the plot is defined by n. Nuclei in the IHC images are shown in blue. The size of the spheroids is marked with a white scale bar of 100 μm. Data is shown as median with interquartile range. The width of each curve corresponds with the approximate frequency of data points in each region. All experiments were conducted with Donor 1 as the PHH donor and with two different NPC donors, either Donor 6 or Donor 7. Differences were tested using the student's t test.