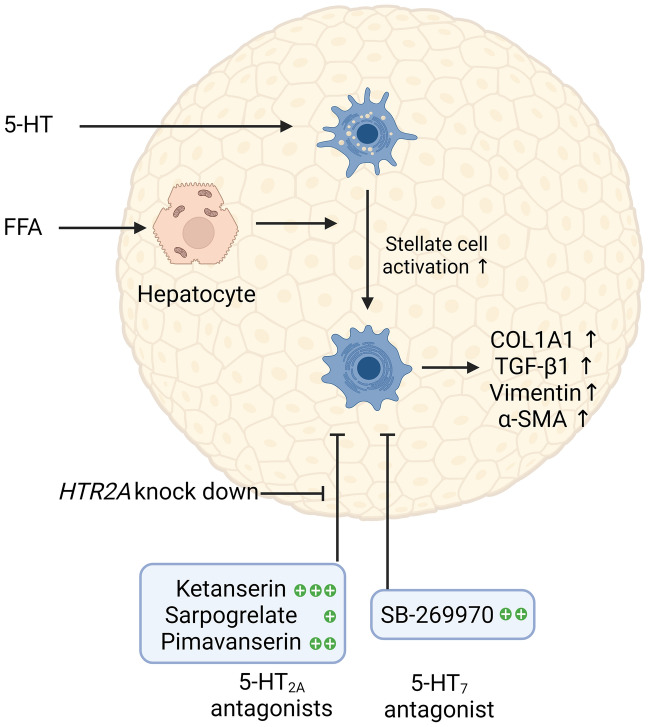
Figure 6.
A schematic presentation of the importance of 5-HT signalling in liver fibrosis. Both FFA and 5-HT induced fibrosis in the spheroids, comprised of PHH and NPC, presumably through the activation of hepatic stellate cells. Fibrotic phenotype presented with increased deposition of COL1A1, as well as with increased production of TGF-β1, vimentin, and α-SMA. 5-HT receptor antagonists were tested for their anti-fibrotic capacity. FFA-induced fibrosis was decreased by all four tested 5-HT receptor antagonists. However, ketanserin showed the strongest anti-fibrotic characteristics. Anti-fibrotic activity of the tested 5-HT2A antagonists can be blocked by knocking down the receptor. Results of the study emphasize the importance of 5-HT signalling in liver fibrosis development, as well as warrant further search for novel targets for liver fibrosis treatment among members of the 5-HT pathway. 5-HT serotonin, COL1A1 collagen, type I, α1, FFA free fatty acids, NPC non-parenchymal cells, PHH primary human hepatocytes, TGF-β1 transforming growth factor beta 1. Created with BioRender.com.