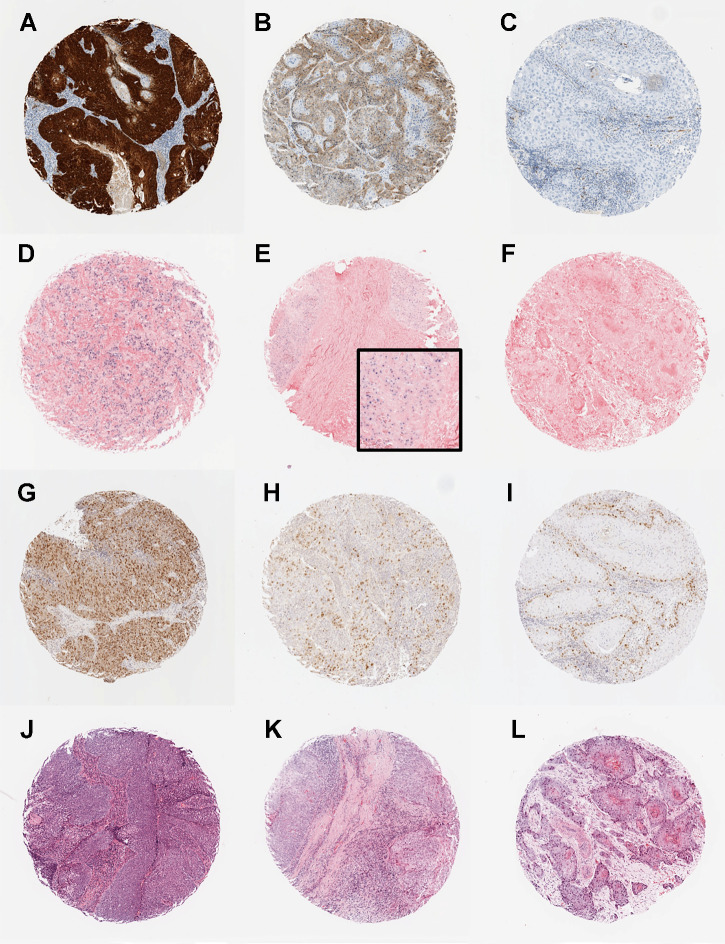
Figure 1.
Photomicrographs showing examples of the biomarkers in the predictive classifier: p16 immunohistochemistry (A–C), high-risk HPV in situ hybridization (D–F), survivin immunohistochemistry (G–I), and TILs (J–L). A, p16-positive tumor showing strong and diffuse nuclear and cytoplasmic staining. B, p16-negative tumor showing weak and diffuse cytoplasmic staining. C, p16-negative tumor with no staining. D–E, High-risk HPV-positive tumors showing diffuse nuclear and cytoplasmic staining (D) and punctate nuclear staining (E). F, High-risk HPV-negative tumor with no staining. G–I, Survivin staining showing tumors with high (G), medium (H), and low (I) H-scores. J–L, Cases with high (J), moderate (K), and low (L) TILs.