Fig. 4.
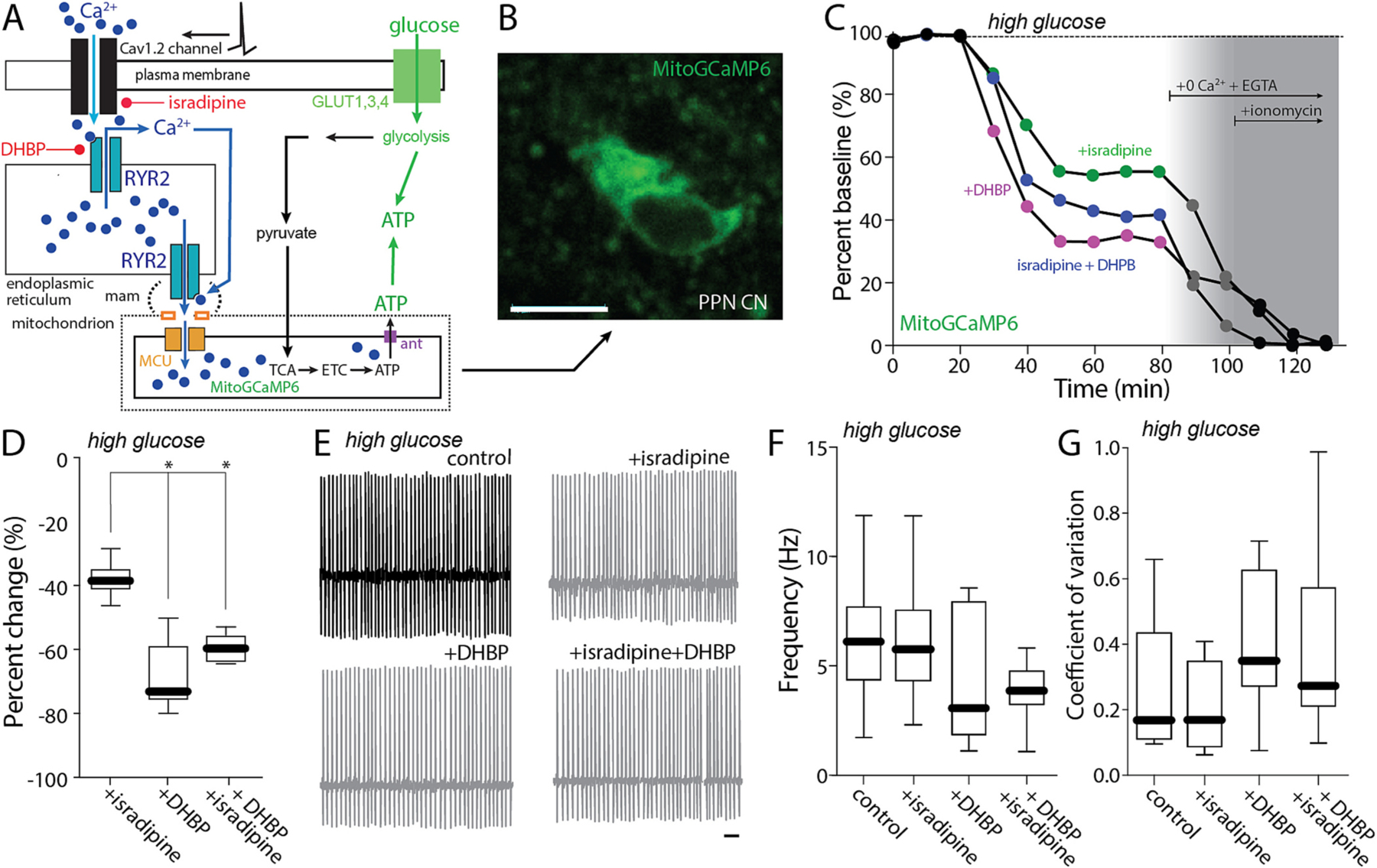
Cav1 block effect on pacemaking is mediated by control of mitochondrial matrix Ca2+ content. A. Cartoon illustrating the effect of Ca2+ entry through Cav1.2 channels on RYR Ca2+ release in a high-glucose (25 mM) aCSF. B. Representative micrograph of a recorded PPN CN expressing mitoGCaMP6. Bar: 10 μm. C. Representative examples of the percentage of mitochondrial Ca2+ in a PPN CN before and after addition of isradipine (500 nM), DHBP or both, 0 Ca2+ + EGTA and 0 Ca2+ + EGTA + ionomycin, all in a high-glucose (25 mM) aCSF. D. Percentage of change of mitochondrial Ca2+ from aCSF for isradipine, DHBP and both (Kruskal-Wallis, Interaction: *p < 0.0001; Dunn’s multiple comparison, Isradipine-DHBP: *p = 0.0016; Isradipine-Isradipine+DHBP: #p = 0.0520; n = 6 in each group). E. Representative cell-attached recordings of PPN CNs without or with chronic isradipine (500 nM, 1 h pre-incubation), chronic DHBP (100 μM, 1 h pre-incubation), or both, in the presence of picrotoxin (100 mM) and CNQX (50 mM) in a high-glucose (25 mM) aCSF. Bar: 1 s. F-G. Firing frequency (F) and coefficient of variation (G) of PPN CNs with or without isradipine, DHBP, or both (F: Non-parametric one-way ANOVA, interaction NS; Dunn’s multiple comparison: control-Isradipine: NS; control-DHBP: NS; control-Isradipine+DHBP: NS; Isradipine-DHBP: NS; Isradipine-Isradipine+DHBP: NS; DHBP-Isradipine+DHBP: NS. G: Non-parametric one-way ANOVA, interaction NS; Dunn’s multiple comparison: control-Isradipine: NS; control-DHBP: NS; control-Isradipine+DHBP: NS; Isradipine-DHBP: NS; Isradipine-Isradipine+DHBP: NS; DHBP-Isradipine+DHBP: NS; n = 9 in each group). Box plots indicate first and third quartiles, thick center lines represent medians, and whiskers indicate the range.
