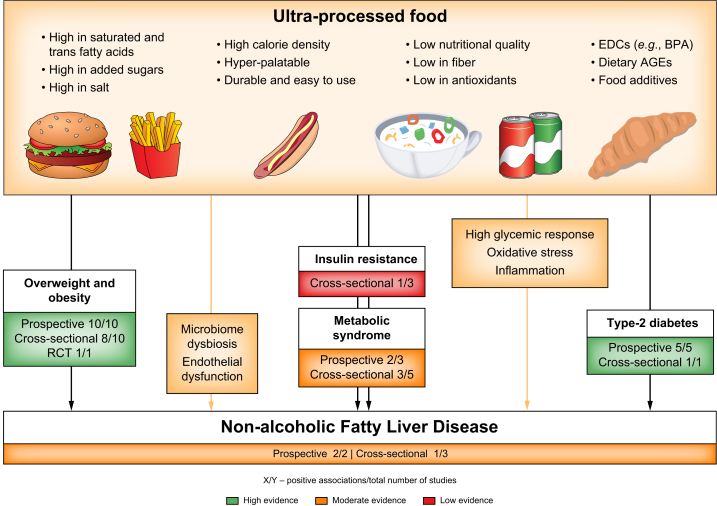
Fig. 2.
Ultra-processed food consumption and NAFLD, its major risk factors, and plausible mechanisms underlying the associations.
The effect of UPF on NAFLD can be explained through several pathways. First, the poor nutritional value of UPF. Second, non-nutritional food compounds or additives within UPF (e.g., EDCs and AGEs) through their pro-oxidative and proinflammatory properties. Lastly, dietary factors common in UPF were found to alter gut microbiome composition (dysbiosis), including saturated fatty acids, fructose, and food additives. AGEs, advanced glycated end products; BPA, bisphenol A; EDCs, endocrine-disrupting chemicals; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; UPF, ultra-processed food.