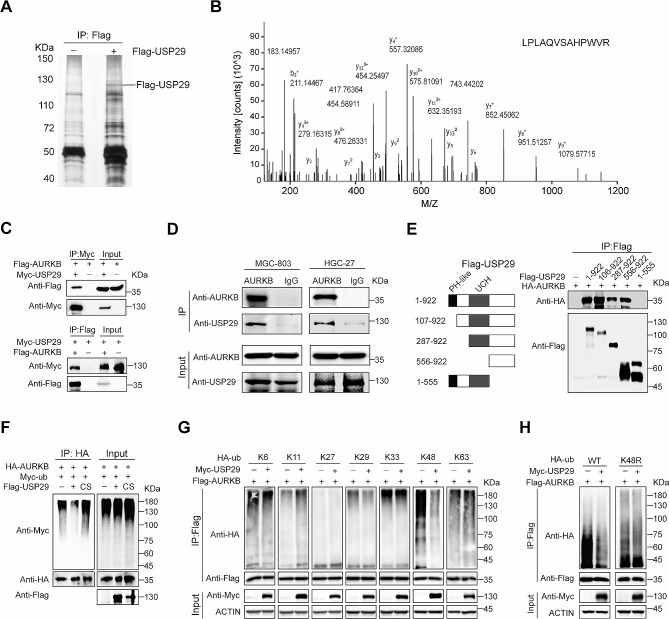
Fig. 2.
USP29 interacts with AURKB and removes its K48-linked polyubiquitination. (A) Immunoprecipitation of Flag-USP29 using anti-Flag antibody. Total cell proteins extracted from MGC-803 cells expressing Flag-tagged USP29 or vector alone were subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-Flag beads, which were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining. (B) Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of the Flag-USP29-associated peptides corresponding to AURKB. (C) 293T cells overexpressing Myc-USP29 and/ or Flag-AURKB were subjected to reciprocal Co-IP to detect protein interaction. (D) Lysates from MGC-803 and HGC-27 cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation using AURKB antibodies, and USP29 was detected by immunoblot. (E) Left: A schematic representation of various Flag-USP29 truncations; right: lysates from 293T cells overexpressing HA-AURKB and respective Flag-USP29 truncation were subjected to Co-IP and immunoblot. (F) 293T cells were co-transfected with HA-AURKB, Myc-Ub and Flag-USP29/USP29 C294S mutant (CS), and polyubiquitination analysis of AURKB was shown. G and H. 293T cells were co-transfected with indicated Flag-AURKB, Myc-USP29, HA-Ub (WT) and various HA-Ub mutant plasmids, polyubiquitination analysis of AURKB was analyzed. The experiments were independently repeated three times with similar results (A, C-D, right of E, F–H)