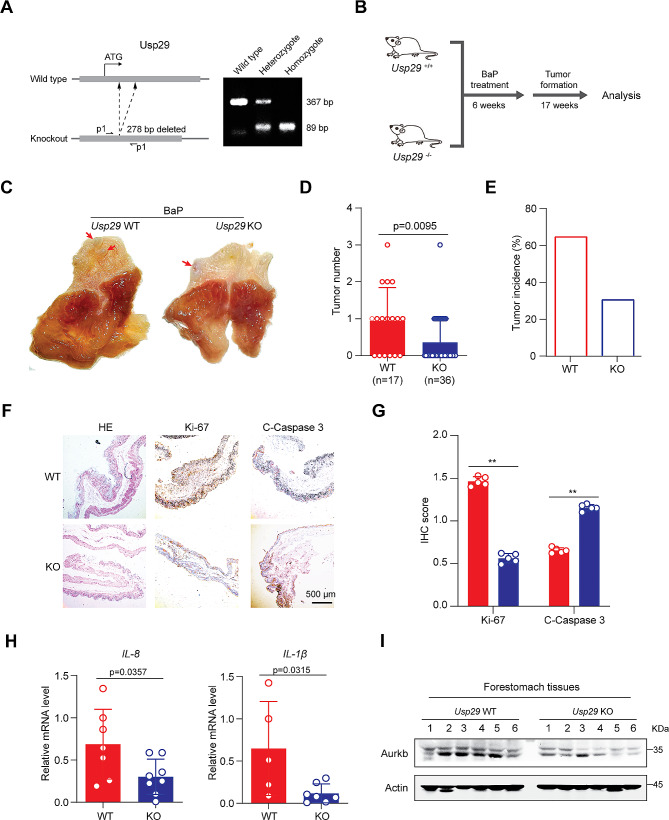
Fig. 5.
Usp29 knockout inhibits gastric tumor formation induced by BaP Treatment. (A) Left: sgRNA targeting strategy to knockout Usp29 allele in mice; right: representative genotyping of wildtype and Usp29 knockout mice. (B) Schematic representation of BaP-induced forestomach carcinogenesis. (C) Representative images showing gross morphology of stomachs harboring BaP-induced tumors (23 weeks) from wildtype and Usp29−/− mice. D and E. Tumor number (D) and tumor incidence (E) in stomachs of WT and Usp29−/− mice after administration of BaP (23 weeks). (F and G). Representative images (F) and quantification (G) of HE, Ki-67, and cleaved caspase-3 staining in WT and USP29−/− tumors. (H). IL-8 and IL-1β mRNA levels in WT and Usp29−/− stomachs harboring BaP treatment were analyzed by RT-qPCR. Graph shows mean ± SD from triplicates; significance was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. (I). AURKB protein expression in WT and Usp29−/− stomachs harboring BaP treatment were analyzed by immunoblots. **p < 0.01