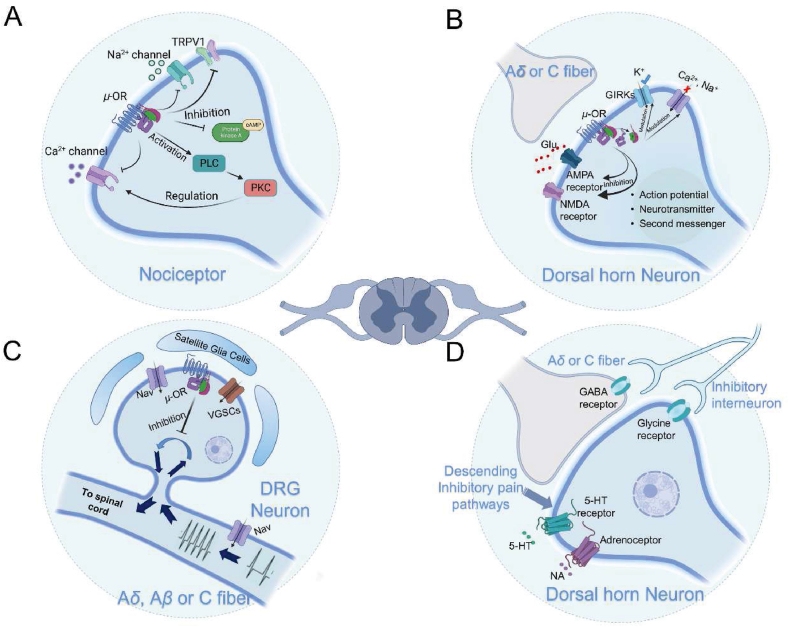
Figure 4.
Mechanisms of analgesic action of μ-opioid receptor in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS). (A) In nociceptive receptors, the activation of μ-opioid receptor (μ-OR) reduces the release of nociceptive substances and decreases Ca2+ production following nerve injury by interacting with TRPV1, H1R, and NK1R. (B) In dorsal root ganglion neurons, μ-OR inhibits the transmission of nociceptive information to the central nervous system by blocking Nav and VGSCs. (C) In spinal dorsal horn neurons, μ-OR induces cell membrane hyperpolarization by inhibiting Nav and VGSCs-mediated Ca2+ influx and activating GIRKs-mediated K+ influx. Moreover, μ-OR modulates ionotropic glutamate receptors, resulting in central analgesic effects. (D) The downstream pain inhibitory pathway activated by μ-OR inhibits the upstream transmission of nociceptive information by modulating 5-HT and norepinephrine receptors, as well as glycine receptors, on spinal dorsal horn neurons.