Fig 3. Hypothesis for effect of risk alleles in HLA-C on KD pathogenesis.
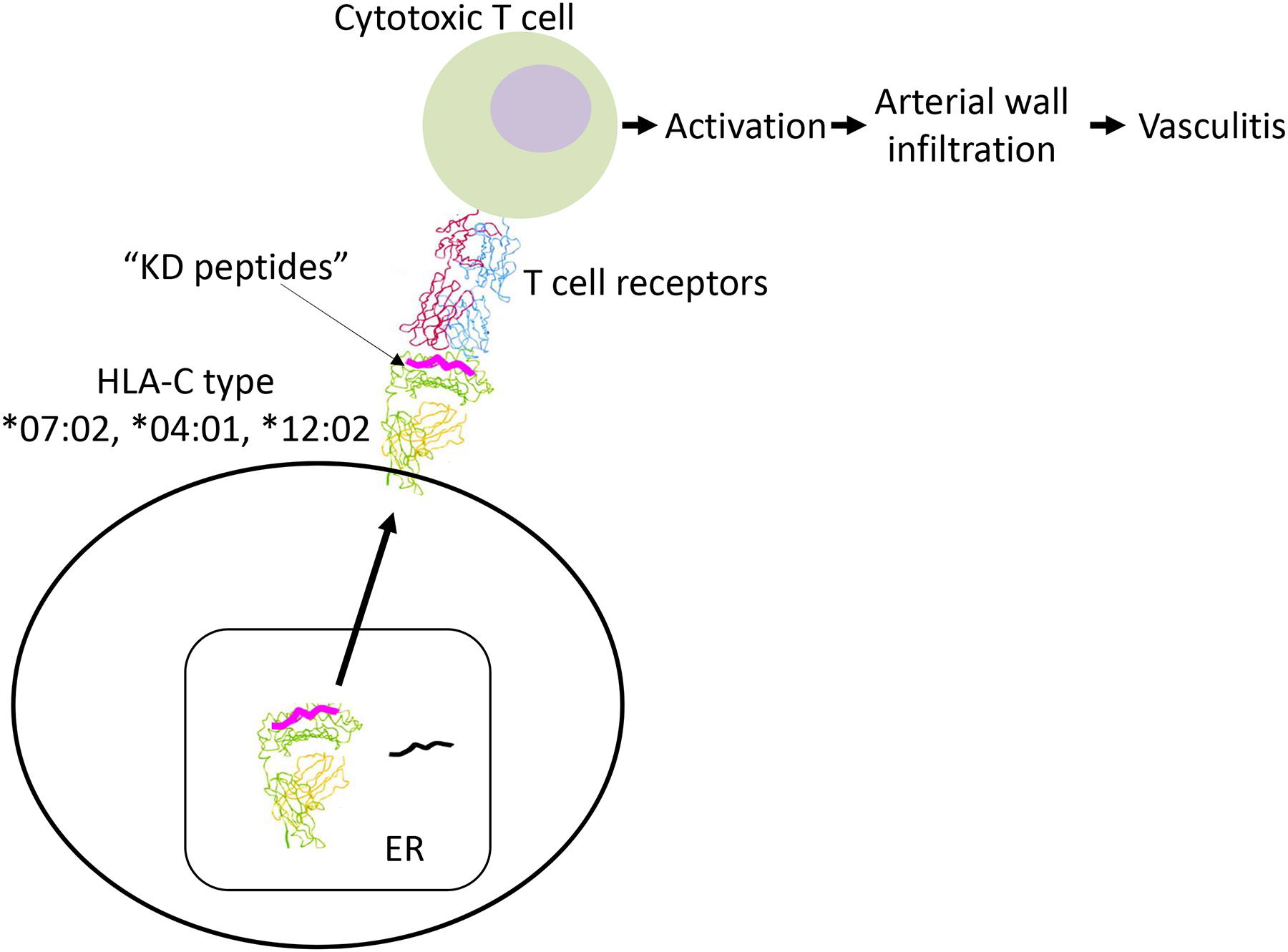
We propose distinct mechanisms by which the risk alleles described here may affect KD susceptibility due to preferential binding of KD pathogen-derived peptides in the HLA-C antigen binding groove. The amino acids associated with the HLA-C risk allele may preferentially bind to KD antigen-derived peptides leading to T cell activation and arterial wall infiltration of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells. ER: endoplasmic reticulum
