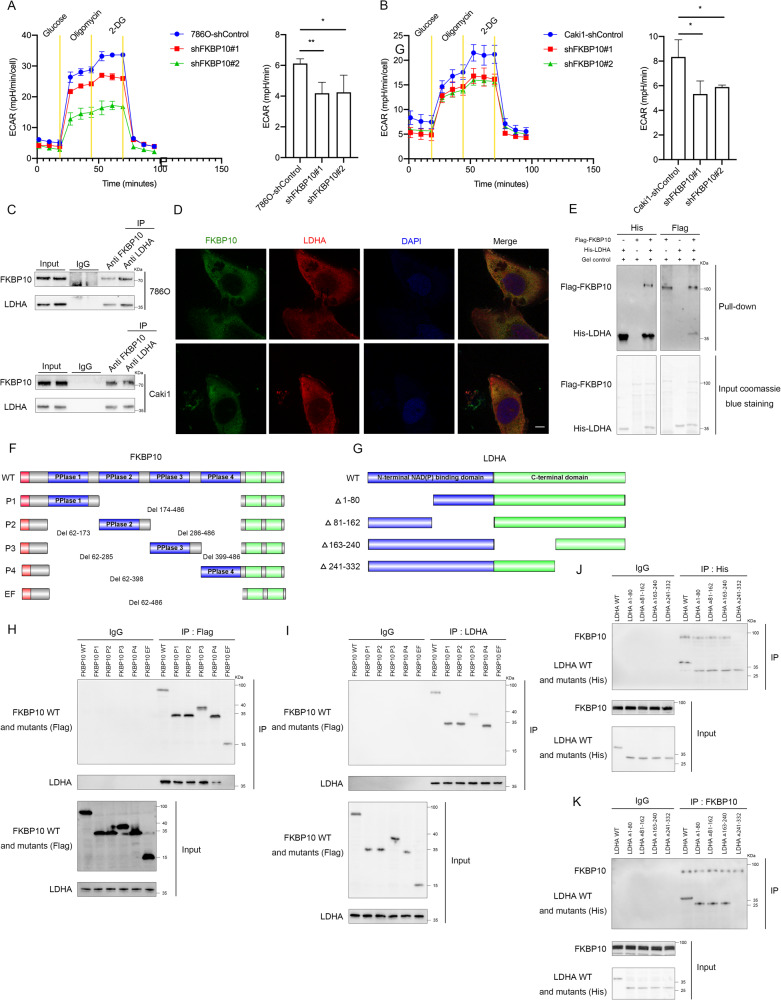
Fig. 3. FKBP10 can directly bind with LDHA.
A, B Extracellular acidification (ECAR) of 786 O and Caki1 cells with FKBP10 knockdown. Data are presented as the means ± SD and were independently replicated three times. C, D Immunoprecipitation analyses of the binding of endogenous FKBP10 and LDHA in 786 O and Caki1 cells. The cellular localizations of FKBP10 and LDHA were analyzed by immunofluorescence (magnification ×100). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 10 µm. E In vitro pull-down assays indicated that FKBP10 directly bound with LDHA. F Schema of deletion mutants of FKBP10. Domains illustrated include signal peptide (red), PPlase (blue), and EF hand (green). G Schema of LDHA deletion mutants. The N-termini are labeled in blue, and the C- termini are green. H, J Co-IP assays of exogenous FKBP10 with different LDHA fragments or exogenous LDHA with different FKBP10 mutations in HEK293 cells. IgG was used as a negative control for immunoprecipitation. I, K Co-IP analyses of the interaction between various regions of FKBP10 and endogenous LDHA or various regions of LDHA and endogenous FKBP10 in 786 O cells. IgG served as the negative control. Statistical analyses were performed with a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).