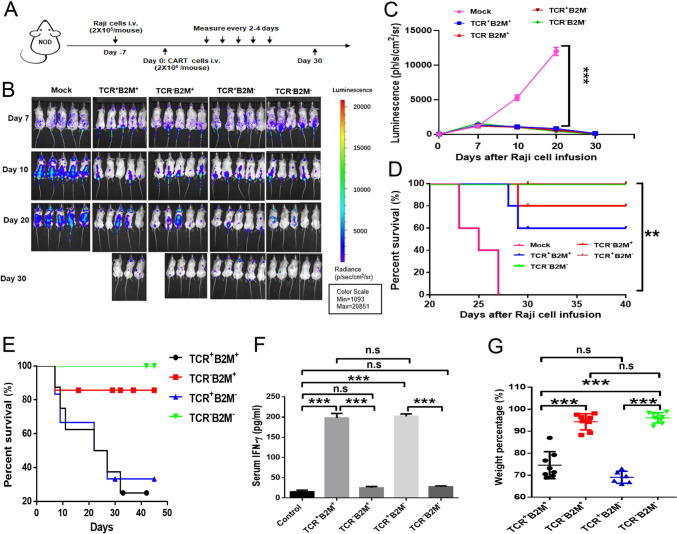
Fig. 2.
Antitumor ability of U-CAR-T19 cells in an animal model. a Schematic of the Raji xenograft tumor model; 8-week-old B-NDG (NOD.CB17-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1/Bcgen) male mice were inoculated intravenously with ffLuc-transduced Raji cells (2 × 105 cells/mouse), and 2 × 106 TRAC or B2M-gene-edited CAR-T cells were administered intravenously after 7 days (n = 5 mice per group). The IVIS Lumina II In Vivo Imaging System was used to monitor tumor growth every 2–4 days. b Fluorescence of each group mice treated with different gene-edited CAR-T19 cells. c Averages of bioluminescence in each group mouse treated with different CAR-T19 cells. d The survival of each group of mice was assessed, CAR-T cells treated groups had a prolonged survival. e–g The NSG mice were treated with different gene-edited CAR-T19 cells for the GVHD assay. Survival (e), serum IFN-γ (f), and body weight change (g) of treated mice were assessed. Statistical significance, ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test or two-tailed, paired Student’s t test were used, n.s, no significance, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001