Figure 5.
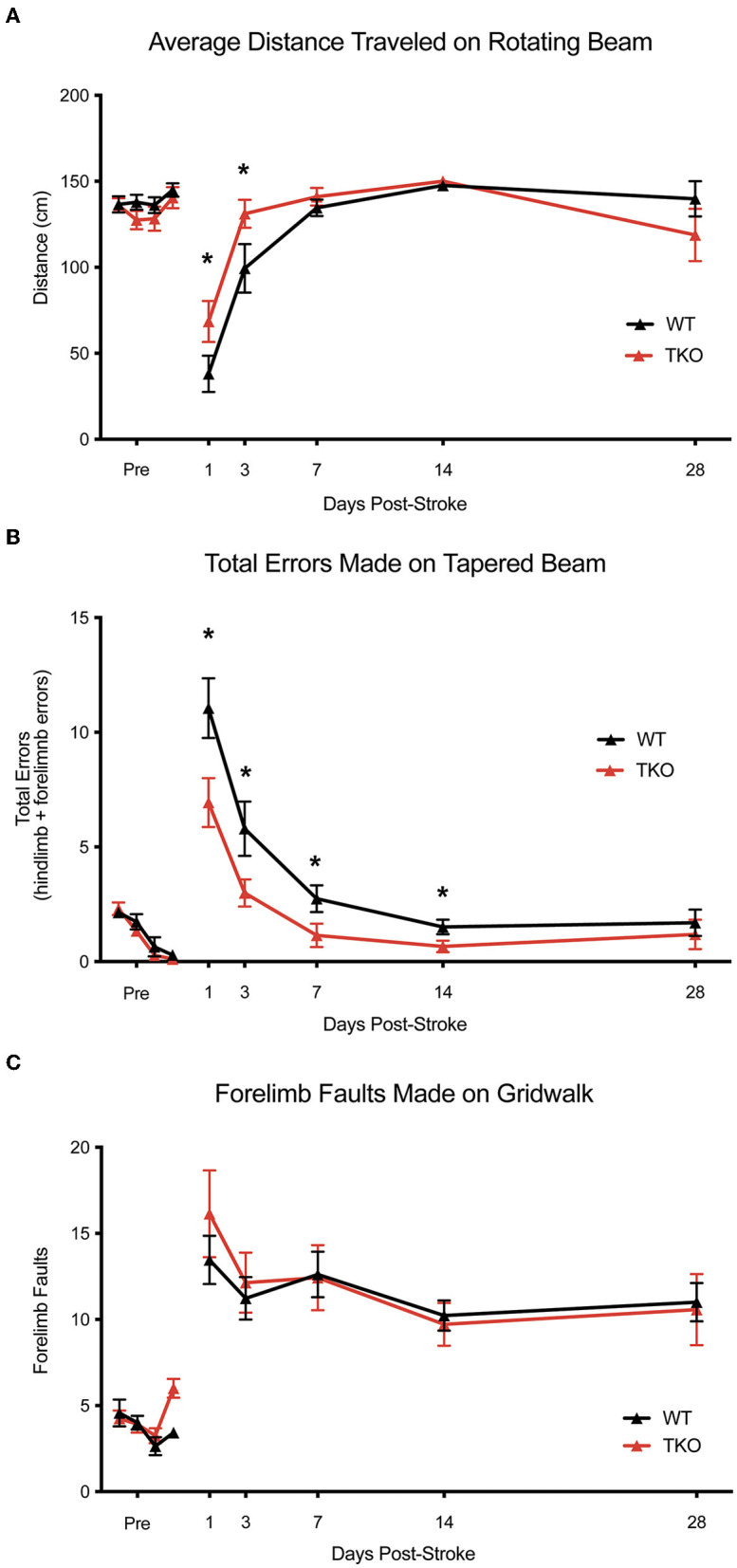
TNF, IL1α, and C1q deletion reduces behavioral deficits after ischemic stroke. (A) Tnf−/−Il1a−/−C1q−/− triple knockout (TKO) mice a significantly further distance on the rotating beam as the wildtype (WT) mice, F(1, 24) = 0.3969, p = 0.026. A post-hoc analysis revealed that TKO mice made fewer errors 1- (p = 0.0358) and 3 days (p = 0.0244) after stroke. (B) TKO mice mad significantly fewer errors on the tapered beam task than WT mice, F(1, 24) = 6.342, p = 0.0189. A post-hoc analysis revealed that TKO mice made fewer errors 1- (p < 0.0124), 3- (p < 0.023), 7- (p < 0.0329), and 14 (p < 0.0453) days after stroke. (C) TKO mice and WT mice made a similar number of contralateral forelimb errors on the grid walk task, F(1, 32.008) = 0.015, p = 0.91. * p < 0.05. TKO, Tnf−/−Il1a−/−C1q−/− triple knockout mouse; WT, wild type.
