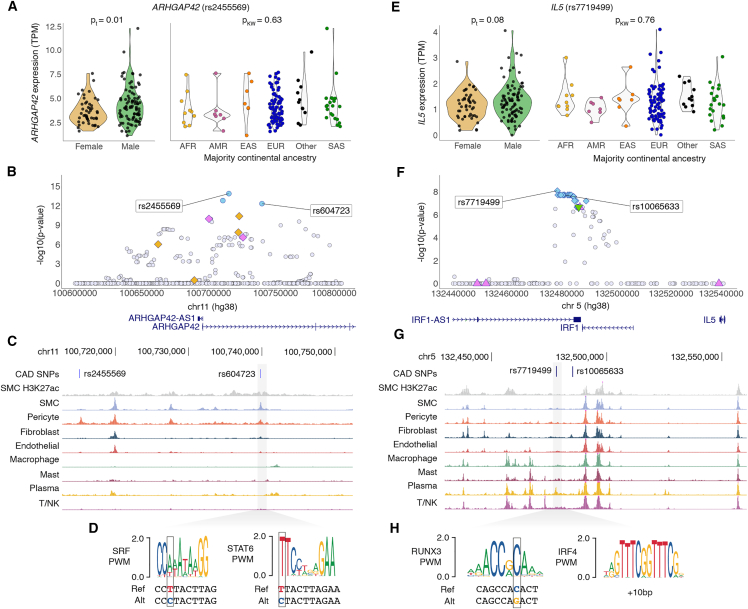
Figure 4.
Fine-mapping identifies candidate causal variants for ARHGAP42 and IL5 eQTLs at known GWAS loci
(A) ARHGAP42 association driven by lead eQTL rs2455569, exhibiting differences in expression by genotype but not sex or majority continental ancestry. p values calculated from paired t test (t) or Kruskal-Wallis test (KW).
(B) Regional association plot depicting variants in PAINTOR credible sets specific to BP (violet) or CAD (golden) GWAS annotations, mixFine only (light blue), and variants not in any credible set (light gray).
(C) Variants of interest (rs604723 and rs2455569) are indicated by blue lines, and rs604723 is highlighted in gray box and corresponds to UCSC Genome Browser tracks indicating cell-type-specific chromatin accessibility.
(D) Location of rs604723 in critical nucleotides (in gray outlined boxes) of consensus transcription factor binding sequences for SRF and STAT6 as identified using the JASPAR 2022 database.
(E) IL5 association driven by lead eQTL rs7719499, exhibiting differences in expression by genotype but not sex or majority continental ancestry. p values calculated from paired t test (t) or Kruskal-Wallis test (KW).
(F) Regional association plot depicting variants in PAINTOR credible sets specific to BP (violet) or CAD (golden) GWAS annotations, mixFine only (light blue), mixFine and PAINTOR CS (green), and variants not in any credible set (light gray).
(G) Variants of interest (rs7719499 and rs10065633) are indicated by blue lines, and rs7719499 is highlighted in gray box and corresponds to UCSC Genome Browser tracks indicating cell-type-specific chromatin accessibility.
(H) Location of rs7719499 in critical nucleotides (in gray outlined boxes) of consensus transcription factor binding sequences for RUNX3 and nearby IRF4 (+10 bp), as identified using the JASPAR 2022 database.