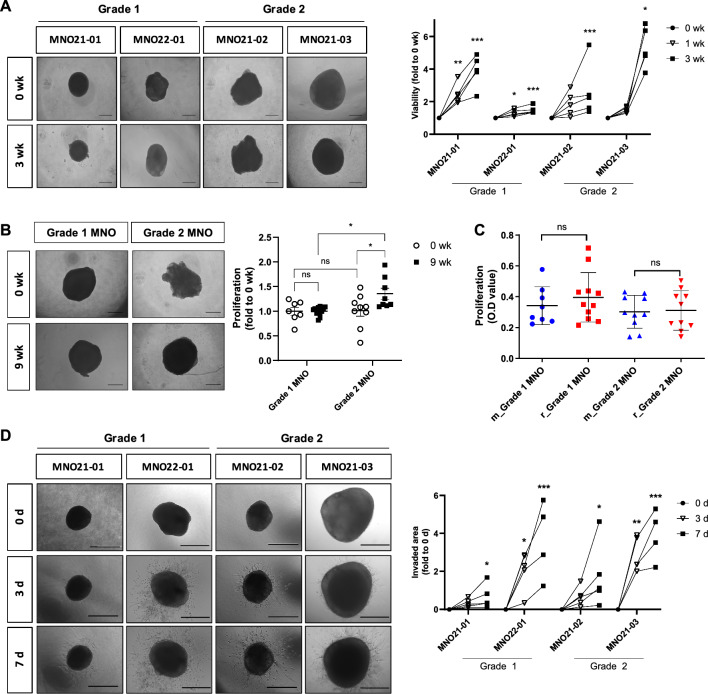
Fig. 2.
Functional characteristics of MNOs. A Bright-field microscopy images of individual growing MNOs. Quantification exhibits proliferation of individual MNOs and was measured by WST assay at each time point. Viability of MNOs was weekly measured by WST assays, and representative figures were captured by bright-field microscopy (Scale bar, 500 μm). Repeated measure ANOVA was performed to evaluate statistical significance compared with the 0 wk control (n = 5 per groups; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). B Long-term culture of MNOs. Viability of MNOs were measured at each time point (0 and 9 wk) by WST assays, and representative figures were captured by bright-field microscopy (Scale bar, 500 μm). Each MNO was cut when they get reached to diameters > 2 mm and could not be applied to paired comparison due to long-term culture. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test was conducted to evaluate statistical significance (*P < 0.05). C Comparison of viabilities between continuously maintained MNOs (m_MNO) and recovered MNOs after cryopreservation (r_MNO). MNOs were recovered from the biobanks of two patients (grade 1: MNO21-01; grade 2: MNO21-02) (n = 8, m_MNO21-01; n = 11, r_MNO21-0; n = 10, m_MNO21-02; n = 10, r_MNO21-02). D Invasiveness of individual MNOs (n = 5) was measured at 3 d and 7 d using 3D invasion assays, and representative figures were captured by bright-field microscopy (Scale bar, 500 μm). Invaded areas were quantified using ToupView software. Repeated measure ANOVA was performed to evaluate statistical significance compared with the 0 d control (n = 5 per groups; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). For A–D, Shapiro–Wilk test was performed to confirm normality of distribution