Figure 5. Electrochemical detection of SARS-CoV-2 variants in human NP/OP biofluid samples.
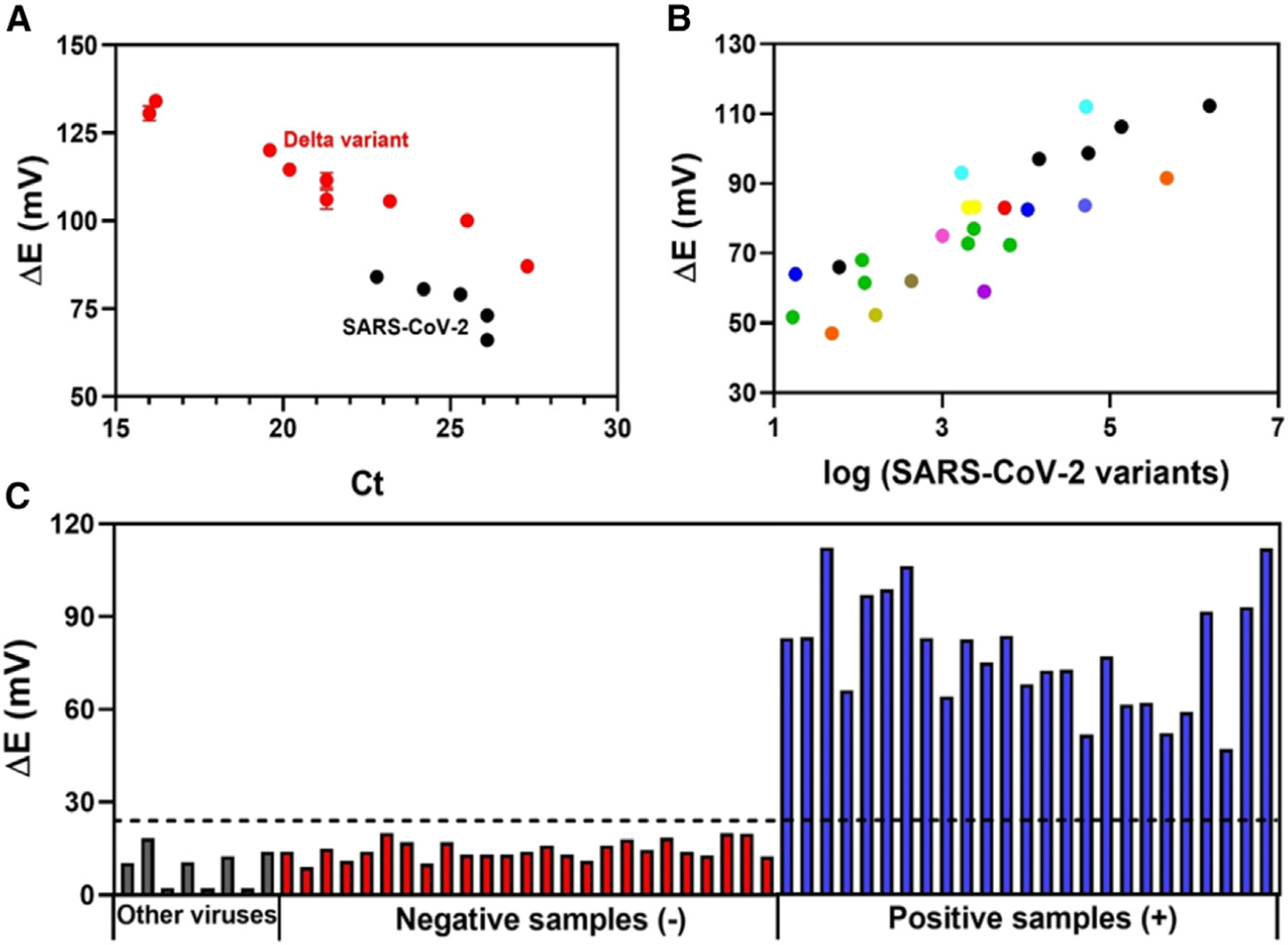
(A) Electrochemical response obtained for five clinical samples containing original SARS-CoV-2 strain (black circles) and 10 clinical samples containing SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant (B.1.617.2, red circles) as a function of Ct values. All measurements were recorded in triplicate (n = 3), and the error bars correspond to the standard deviation.
(B) Potential difference, ΔE, obtained using the modified electrode for another 12 lineages of SARS-CoV-2 as a function of the RNA concentration (copies μL−1) provided by the RT-PCR method,  B.1,
B.1,  B.1.291,
B.1.291,  B.1.369,
B.1.369,  B.1.340,
B.1.340,  B.1.243,
B.1.243,  B.1.311,
B.1.311,  B.1.1.304,
B.1.1.304,  B.1.1.317,
B.1.1.317,  B.1.2,
B.1.2,  B.1.1.7,
B.1.1.7,  B.1.240, and
B.1.240, and  B.1.350.
B.1.350.
(C) Comparison of the electrochemical response obtained by the cross-reactivity studies (gray bars), 25 SARS-CoV-2-negative clinical samples (red bars), and 25 positive SARS-CoV-2 clinical samples containing different lineages (blue bars). The dotted line indicates the cutoff value of ΔE (V) (ΔE (V) = Esample − Eblank) response established to indicate whether the sample was positive for SARS-CoV-2 variants as determined by our biosensor.
