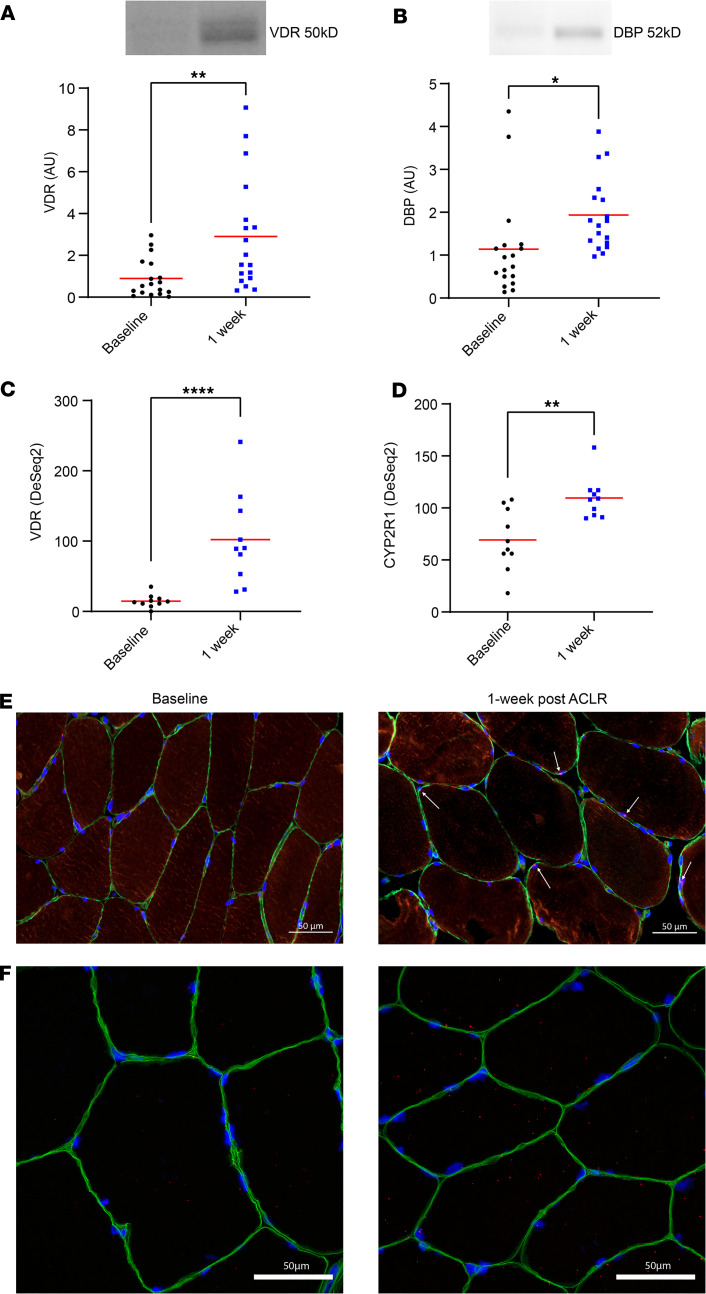
Figure 3. Vitamin D–associated transcripts and proteins in vastus lateralis were elevated in response to ACL reconstruction (ACLR).
(A) Vitamin D receptor (VDR; protein AU) on Western blot increased in response to ACLR (n = 18; P = 0.003). (B) Vitamin D binding protein (DBP) as indicated by Western blots increased from baseline in response to ACLR (P = 0.02). (C) Vitamin D receptor (VDR) RNA-seq transcript count increased from baseline in response to ACLR (n = 10). (D) Cytochrome P450 2R1 (CYP2R1) RNA-seq transcript count increased in response to ACLR. (E) Representative image of VDR protein in IHC analysis of the injured limb at baseline and 1 week after ACLR (1 participant from experiment reported in A). (F) RNAscope in situ hybridization completed to visualize VDR mRNA in the quadriceps of the injured limb at study baseline and 1 week after ACLR. RNAscope was completed on 1 participant showing substantially increased VDR on RNA-seq. Scale bars: 50 μm. Images of individual channels are included in Supplemental Figure 2. One-way repeated-measures ANOVA; results of post hoc tests on graph. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001. Adjusted P values are presented in C and D.