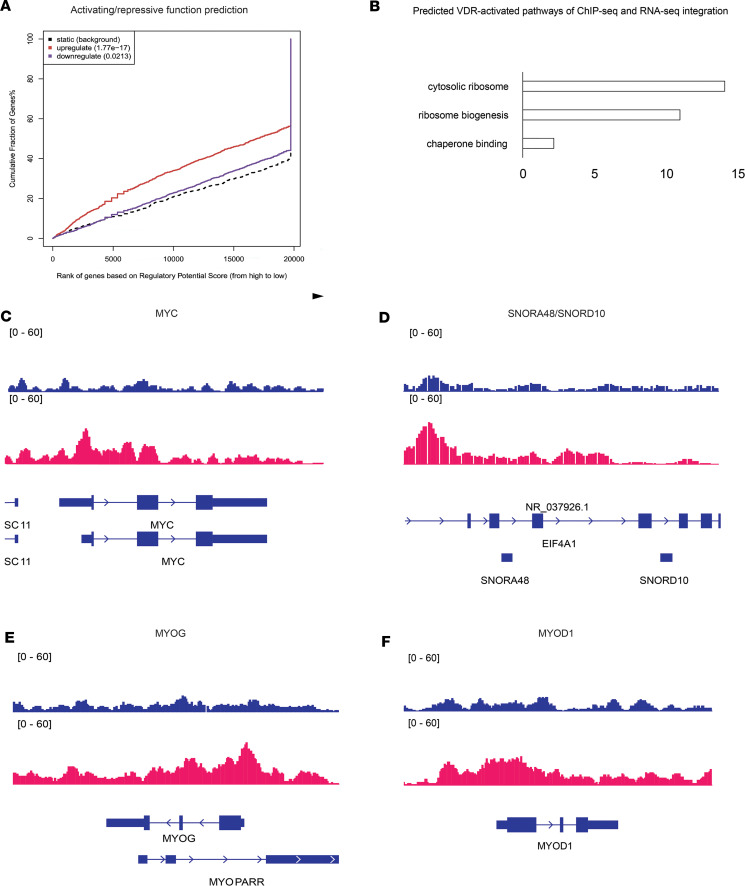
Figure 5. Multiomic integration of ChIP-seq and RNA-seq data implicates the role of VDR in regulating muscle ribosome biogenesis.
(A) ChIP-seq peaks and RNA-seq differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were integrated by calculating an activation and an inhibition score to estimate the effects of transcriptional regulation. Genes are ranked by score and VDR binding is associated with highly significant activation (red solid line) of a subset of DEGs relative to background (black dotted line). The small subset of DEGs showing significant inactivation by VDR binding is represented by the blue solid line. (B) Top 3 enriched biological processes for VDR-activated DEGs. ChIP-seq reads for input (blue, top) and VDR (red) showing VDR binding at the genomic locations for MYC (C), SNORA4B/SNORD10 (D), MYOG (E), and MYOD1 (F). Coding sequence for each gene is shown in blue below the VDR red peaks. Rectangles are exons and arrows along the introns indicate direction of mRNA transcription. Multiple splice isoforms are shown.