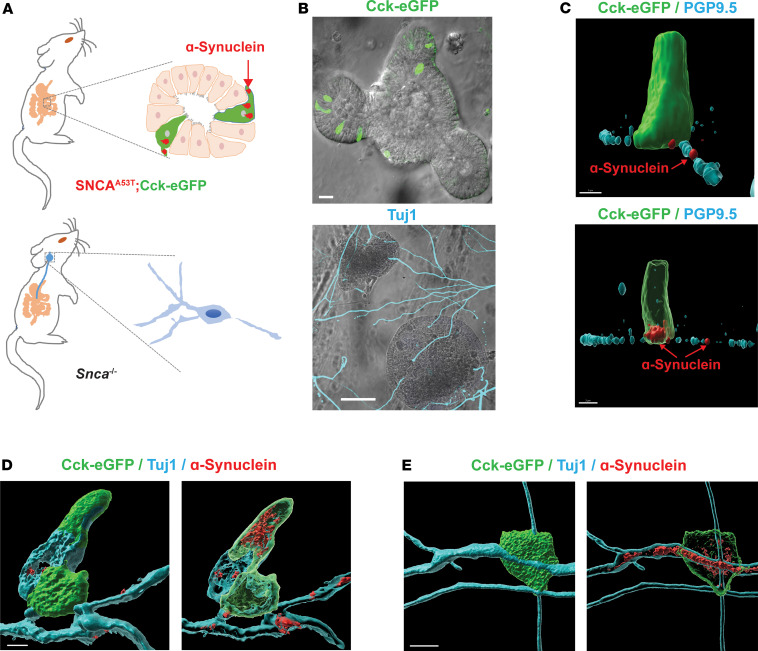
Figure 2. Human A53T α-synuclein protein transfers from gut cells to adjoining vagal neurons.
(A) Intestinal organoids were prepared from an SNCAA53T mouse in which CCK-containing cells express enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP), and vagal nodose ganglia neurons were isolated from an Snca–/– mouse lacking endogenous α-synuclein. (B) Representative images of organoids and neurons grown in coculture for 5 days, with eGFP-positive cells (green) in the organoid and β-tubulin III (Tuj1, cyan) highlighting neuronal processes. (C) Representative high-magnification α-synuclein (red) staining of an eGFP-positive EEC. Red arrow indicates localization to a PGP9.5-positive (cyan) process in an Snca–/– mouse neuron. (D and E) Representative images with neuron-specific β-tubulin III (cyan). Surface and (adjacent) intracellular confocal slices are shown. Scale bars are 30 μm for B, 3 μm for C, and 5 μm for D and E.