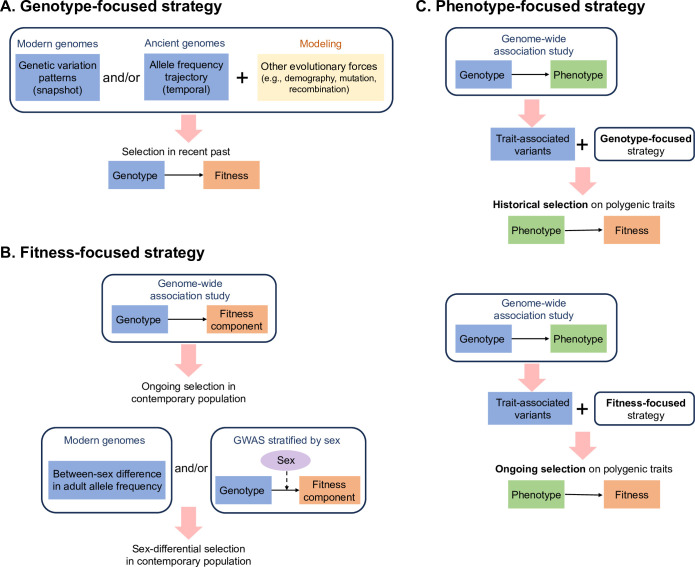
Fig 3. Common strategies for detecting signatures of recent or ongoing selection.
(A) A “genotype-focused” strategy focuses on the cumulative effects of historical selection on genetic variation patterns and relies on population genetics modeling to tease apart the influence of other evolutionary forces. Ancient DNA data provide direct information on allele frequency changes, which helps reduce inference uncertainty and confounding by demographic history. (B) A “fitness-focused” strategy focuses on direct association between genotype and fitness component(s) and utilizes allele frequency changes within one generation to detect selection in contemporary populations. As a special case of this strategy, between-sex differences in adult allele frequency or effect size of association to fitness components can be leveraged to detect sex-differential selection. (C) A “phenotype-focused” strategy relies on aggregation of selection signals revealed by genotype-focused or fitness-focused strategies across trait-associated variants identified by genome-wide association studies (GWAS).