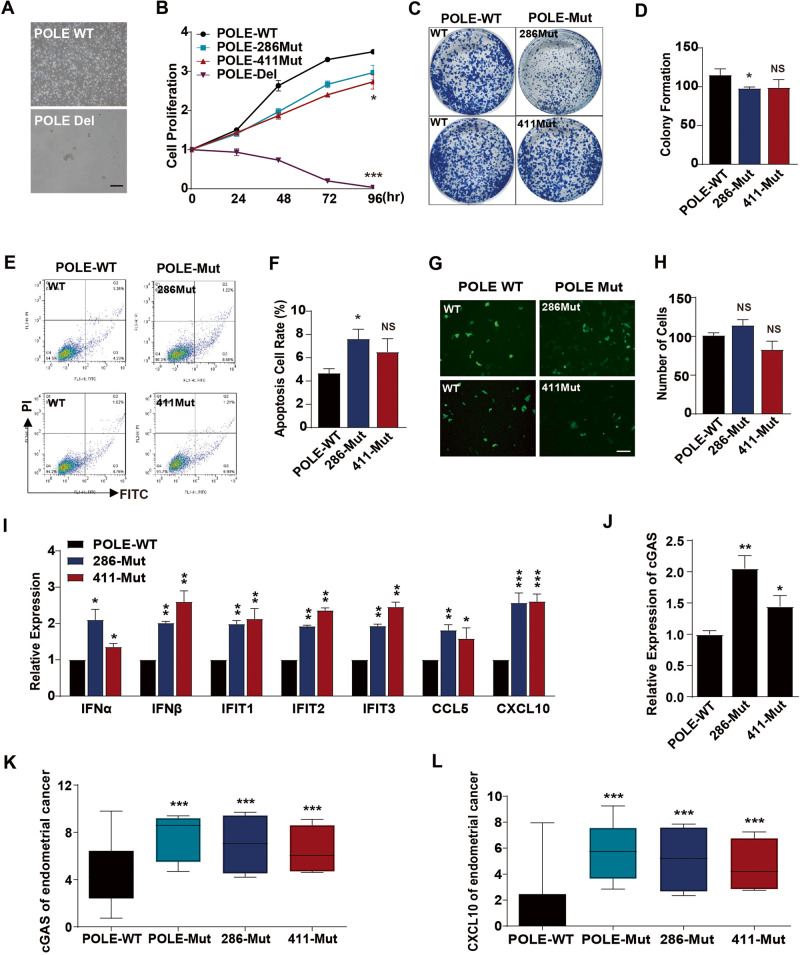
Fig. 2. POLE mutations impede the proliferation and activate inflammatory responses in human EC cells.
A Representative morphologies of WT EC cells and the engineered EC cells with POLE deletion. B CCK8 analyses of WT EC cells and the engineered EC cells with POLE deletion or mutation. C Colony formation assay of WT EC cells and the engineered EC cells with POLE mutation. D Quantification of colony number of EC cells treated as (C). E Apoptosis analysis of EC cells with POLE mutant or WT POLE. F Quantification of the percentages of apoptotic cells in the (E). G Representative images of transwell migration analysis of WT EC cells and the engineered EC cells with POLE deletion or mutation. H Quantification of migrated cells in the (G). I Relative mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines (IFN, IFIT, CCL5, and CXCL10) in WT EC cells and POLE mutant cells. J RT-PCR analysis of cGAS gene in WT EC cells and POLE mutant cells. K Relative mRNA level of cGAS gene in human EC specimens with POLE mutations or WT POLE. L Relative expression level of CXCL10 gene in human ECs with POLE mutation or WT POLE. Data are shown as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.001 significantly different from Control.