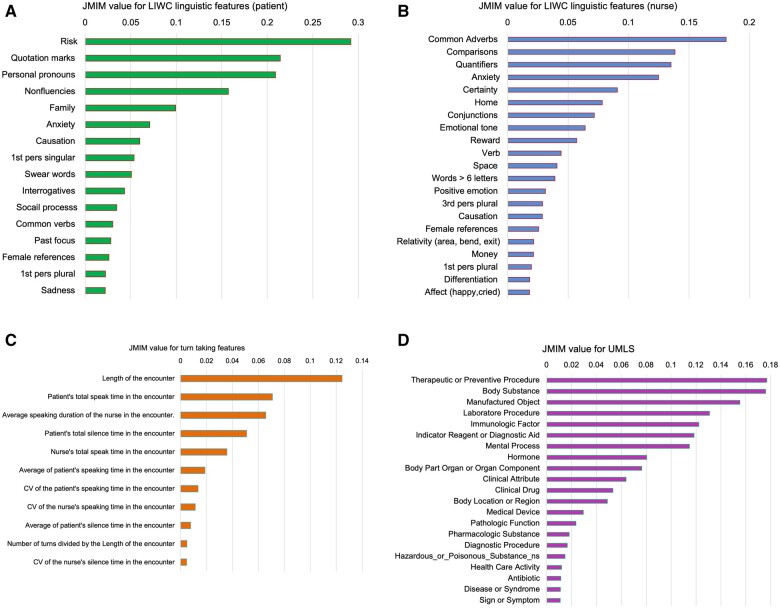
Figure 2.
(A) The most informative features identified using JMIM analysis of LIWC features associated with increased risk of ED visits and hospitalization in patient language. (B) The most informative features identified using JMIM analysis of LIWC features associated with increased risk of ED visits and hospitalization in nurse language. (C) The most informative features identified using JMIM analysis of turn-taking features associated with increased risk of ED visits and hospitalization. (D) The most informative features identified using JMIM analysis of UMLS semantic type features associated with increased risk of ED visits and hospitalization.