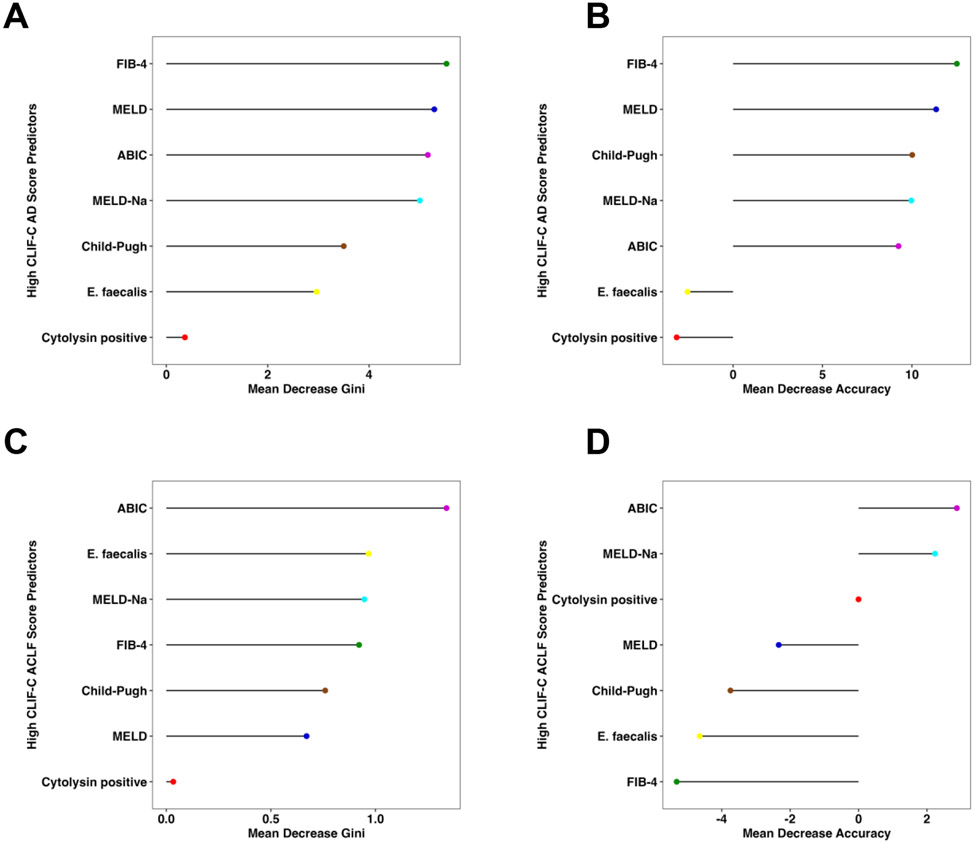
Figure 3. Fecal cytolysin is not an important feature for liver disease severity in cirrhosis with acute decompensation and acute-on-chronic liver failure per random forest analysis.
(A) Mean decrease Gini score and (B) mean decrease accuracy by random forest analysis were quantitated for presence of cytolysin and multiple liver disease markers to determine their respective feature importance for high CLIF-C AD score (Cytolysin n=63, E. faecalis n=63, FIB-4 n=60, ABIC n=63, Child-Pugh=59, MELD score n=63, and MELD-Na score n=63). (C) Mean decrease Gini score and (D) mean decrease accuracy for high CLIF-C AD score (Cytolysin n=15, E. faecalis n=15, FIB-4 n=14, ABIC n=14, Child-Pugh=15, MELD score n=14, and MELD-Na score n=14). ABIC, ‘Age, serum bilirubin, INR, and serum creatinine score’; ACLF, acute-on-chronic liver failure; AD, acute decompensation; CLIF-C, European Foundation for the study of chronic liver failure; FIB-4, Fibrosis-4 Index; INR, international normalized ratio; MELD, model for end-stage liver disease; MELD-Na, sodium-adjusted model for end-stage liver disease.