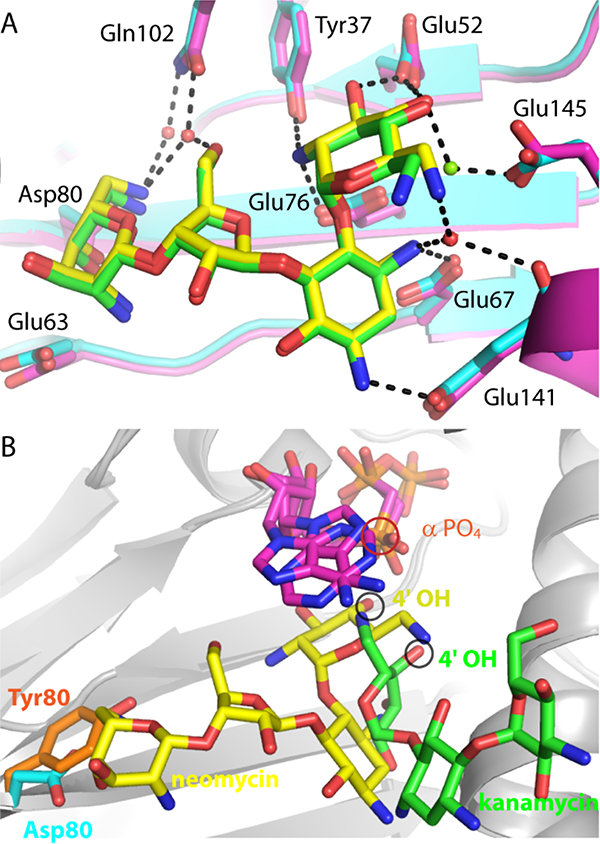
Figure 2.
Comparison of ANT4’ mutant structures. A. Superposition of wild-type ANT4’ (magenta carbon atoms) bound to neomycin (green carbon atoms) with T130K ANT4’ (cyan carbon atoms) bound to neomycin (yellow carbon atoms). Hydrogen bonds to the T130K-neomycin complex are shown as black dashed lines. B. Superposition of D80Y ANT4’ and the T130K ANT4’ ternary complexes. The D80Y ANT4’ mutant is shown with kanamycin (green carbon atoms) and AMPNPP (magenta carbon atoms). The T130K ANT4’ mutant is shown with neomycin (yellow carbon atoms) and AMPCPP (magenta carbon atoms). The 4’ hydroxyl, the site of adenylation, is circled in black, and the alpha phosphate is circled in red.