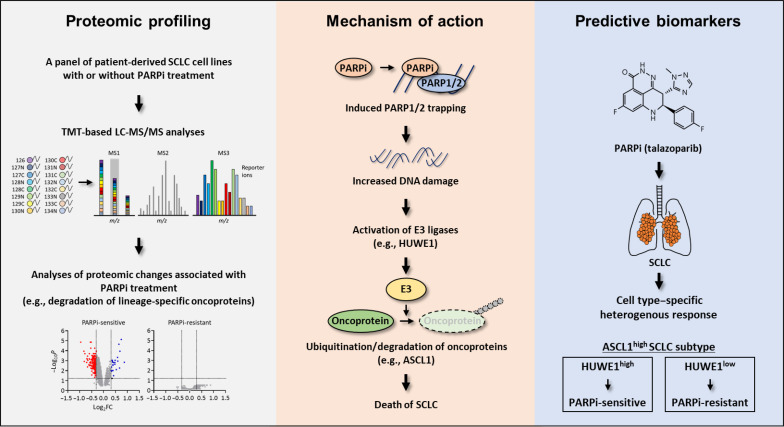
Fig. 6. A Schematic of the workflow in this study.
Proteomic changes were identified that signify PARPi responses in a large panel of molecularly annotated human SCLC cells. The therapeutic vulnerability of SCLC to PARPi in SCLC could be explained, at least in part, by the PARPi-induced degradation of key lineage-specific oncoproteins including ASCL1. Although PARPi resulted in a general DDR in all SCLCs, this signal is sensed differently by individual SCLC cells to generate a cell-specific response. PARPi-induced activation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase HUWE1 mediated the UPS-dependent ASCL1 degradation and eventually, led to SCLC cell death. In addition, PARPi-sensitive ASCL1high SCLC cells expressed significantly higher levels of HUWE1 compared to PARPi-resistant ASCL1high SCLC cells. Therefore, these observations suggested HUWE1 as a potentially predictive biomarker for PARPi.