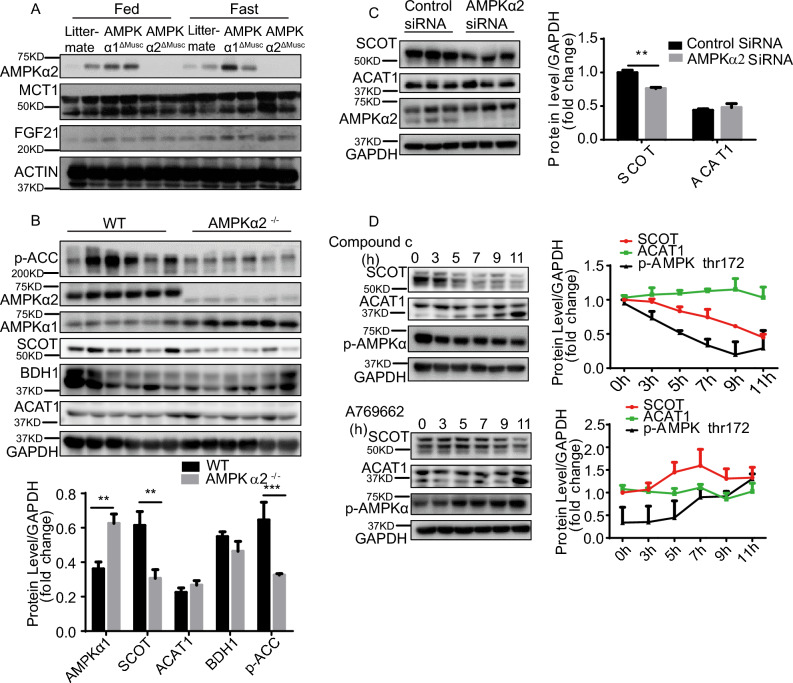
Figure 3.
AMPKα2-mediated fasting-induced hyperketonemia is due to the regulation of SCOT expression in skeletal muscle. (A) Representative western blot images of MCT1, FGF21, and AMPKα2 expression in skeletal muscle of littermate, AMPKα1ΔMusc, and AMPKα2ΔMusc mice after two-day fasting. Beta-actin was used as a loading control. (B) Representative western blot images of AMPKα1, AMPKα2, SCOT, BDH1, ACAT1, and p-ACC in skeletal muscle of WT and AMPKα2–/– mice after two-day fasting (n = 6). GAPDH was used as a loading control. (C) Determination of SCOT, ACAT1, and AMPKα2 in HEK293T cells transfected with control siRNA and AMPK siRNA and harvested after 48 h (n = 3). GAPDH was used as a loading control. (D) Representative western blot images of SCOT, ACAT1, and p-AMPK (T172) in C2C12 cells treated with A769662 (30 µM) and Compound C (10 µM) for 0, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11 h. GAPDH was used as a loading control. Littermate means littermate control mice. Values represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.