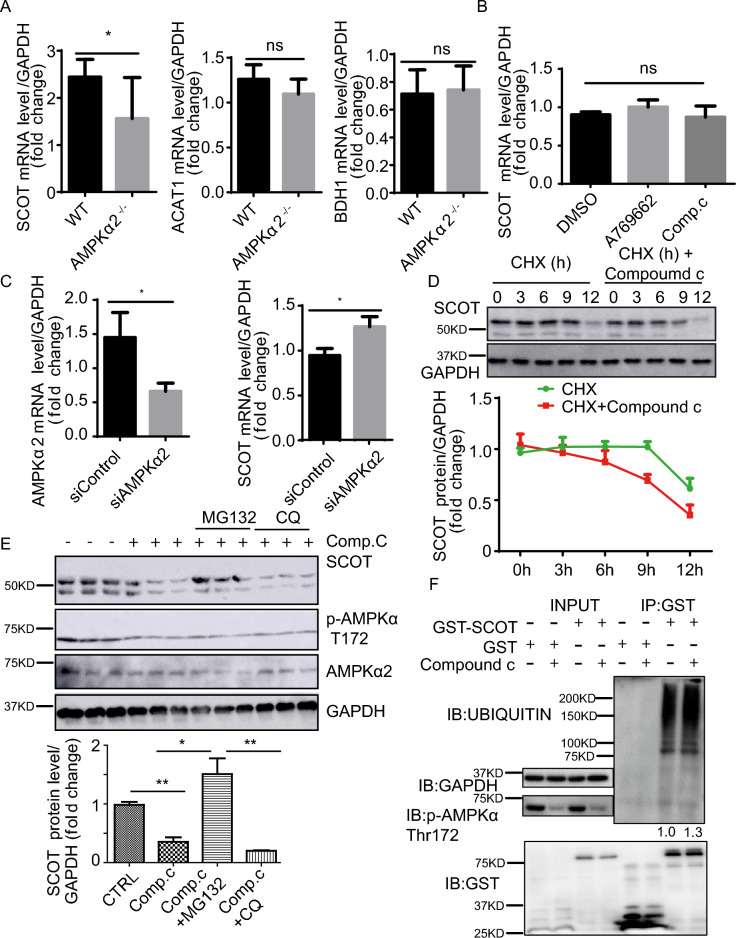
Figure 4.
AMPK inhibits SCOT degradation via the proteosome. (A) Relative SCOT mRNA levels in skeletal muscle in control and AMPKα2–/– mice after 2-day fasting (n = 8). (B) Relative SCOT mRNA levels in C2C12 cells treated with A769662 (30 µM) and Compound C (10 µM) for 6 h (n = 7). (C) Relative SCOT mRNA levels in HEK293T cells transfected with control siRNA and AMPKα2 siRNA and harvested after 48 h of transfection (n = 6). (D) Representative western blot images of SCOT expression in C2C12 cells treated with CHX (10 µg/mL) and CHX (10 µg/mL) plus Compound C (10 µM) and harvested at 0, 3, 6, 9, and 12 h (n = 2). (E) Representative western blot images of SCOT expression in C2C12 cells treated with Comp. C (Compound C,10 µM) or plus MG132 (10 µg/mL) or CQ (10 µg/mL) for 6 h (n = 6). GAPDH was used as a loading control. (F) Representative western blot images of ubiquitinated SCOT and p-AMPK (T172) in HEK293T cells transfected with GST-SCOT for 36 h and treated with 10 µM Compound C for 6 h. Glutathione Sepharose beads were used to pull down the GST-SCOT protein (n = 4). Values represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001.