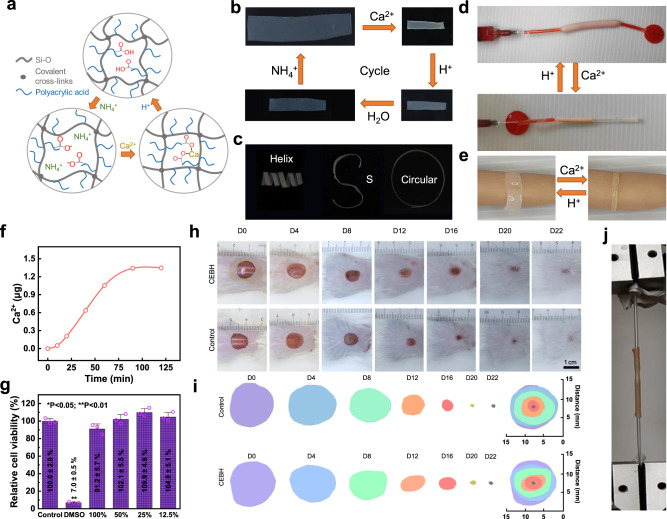
Fig. 4. Shape adaptability of CEBH.
a The conceptional illustration of reversible responses of CEBH. b The ion response process of CEBH in the ammonia, Ca2+, HCl solution, and water. c 3D-shape adaptability of CEBH films via immersing in Ca2+ solution. d Liquid flow control and e shape-adaptive wound dressing using ion-responsive CEBH on a highly simulated silicone skeleton hand model. (The acid environment is supplied with 0.2 M citric acid, and the Ca2+ solution is used to trigger the shrinkage of CEBH. The liquid flowing in the tube was dyed using 0.2% of eosin Y.) f Calcium ion leakage of calcified CEBH in 50 mL ultrapure water. g The viability of L929 cells co-cultured with extraction solution of the calcified CEBH for 24 h (MTT assay). Data are presented as mean values ± SD (n = 3 independent cell experiments). Two-tailed t-tests were performed between experiment groups and the control group, and p values were <0.0001, 0.1145, 0.9653, 0.0701, and 0.5679 for 20% DMSO, and extraction solutions with concentrations of 100%, 50%, 25%, and 12.5%. h Representative photographs and i traces of wound closure of skin wounds treated with Tegaderm filmTM (control group), CEBH (model group) on days 0, 4, 8, 12, 16, 20 and 22. j Tensile test of two tubes connected by shrinking of CEBH in Ca2+ solution. In (a–h), the concentration of ammonia was 0.2%, CaCl2 was 0.1 M, and the AC of CEBH was 62%. In (a–d), the concentration of HCl was 1%.