Fig. 5. Proposed molecular mechanism for RafH action.
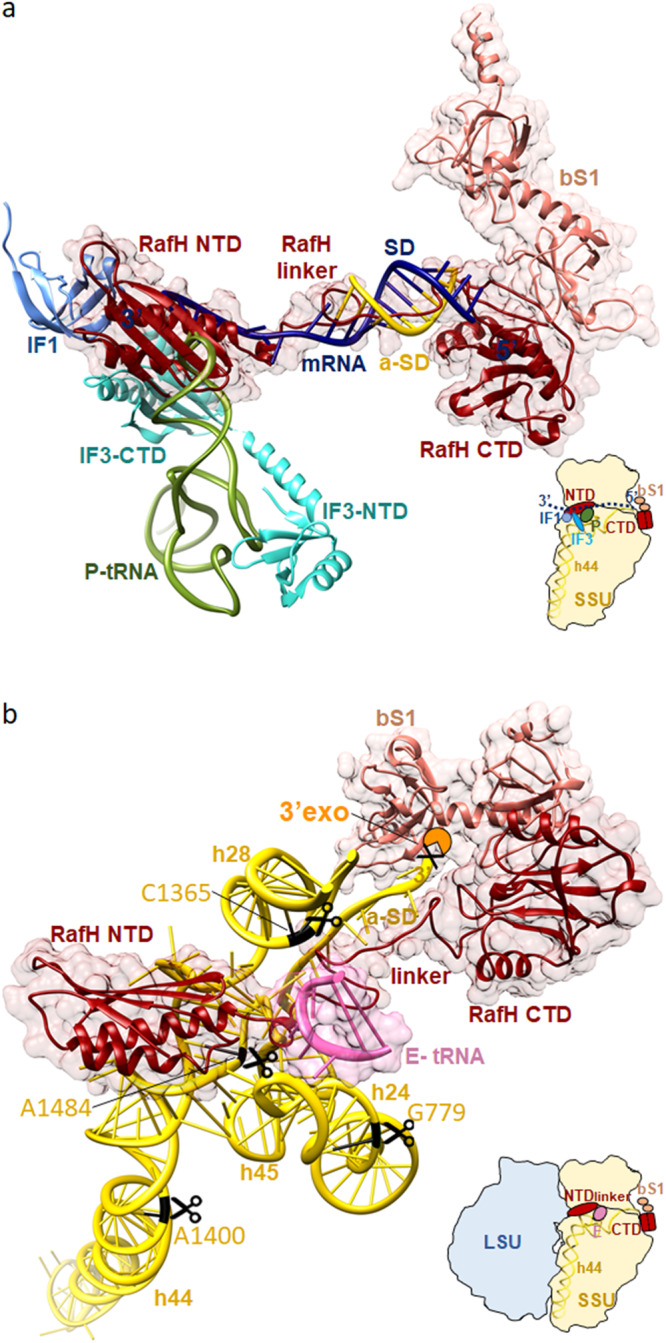
a Inhibition of the translation initiation factor binding by RafH. The pre-translation initiation structure SSU (PDB ID; 5LMT) docked into the ribosome RafH SSU complex structure. For clarity, only the RafH in ribbon (red) with 95% transparent surface, bS1 in ribbon (salmon) with 95% transparent surface, initiation complex factors: mRNA (navy blue), a-SD (gold), IF1 (cornflower blue), IF3 (cyan), and P- tRNA (dark olive green) are shown. A thumbnail is shown in the bottom right. b Protection of 16S rRNA from RNase degradation. The RafH (red) and bS1 (salmon) are shown in ribbon with a 95% transparent surface. 16S rRNA helices, h24, h28, h44, h45, aSD, and 3′ of 16S rRNA are shown in a ribbon with a ladder. The E-tRNA anticodon stem loop (hot pink) is shown in a ribbon with a 95% transparent surface. The RNase nucleolytic site predicted in E. coli 16S rRNA by ref. 15 and corresponding nucleotides in M. smegmatis 16S rRNA are shown in black with the scissors symbol. A thumbnail is shown in the bottom right. The 3′ to 5′ exonuclease RNase PH/RNase R is shown in an orange Pie shape. Its description in 2D is shown in Supplementary Fig. 12.
