Fig. 1.
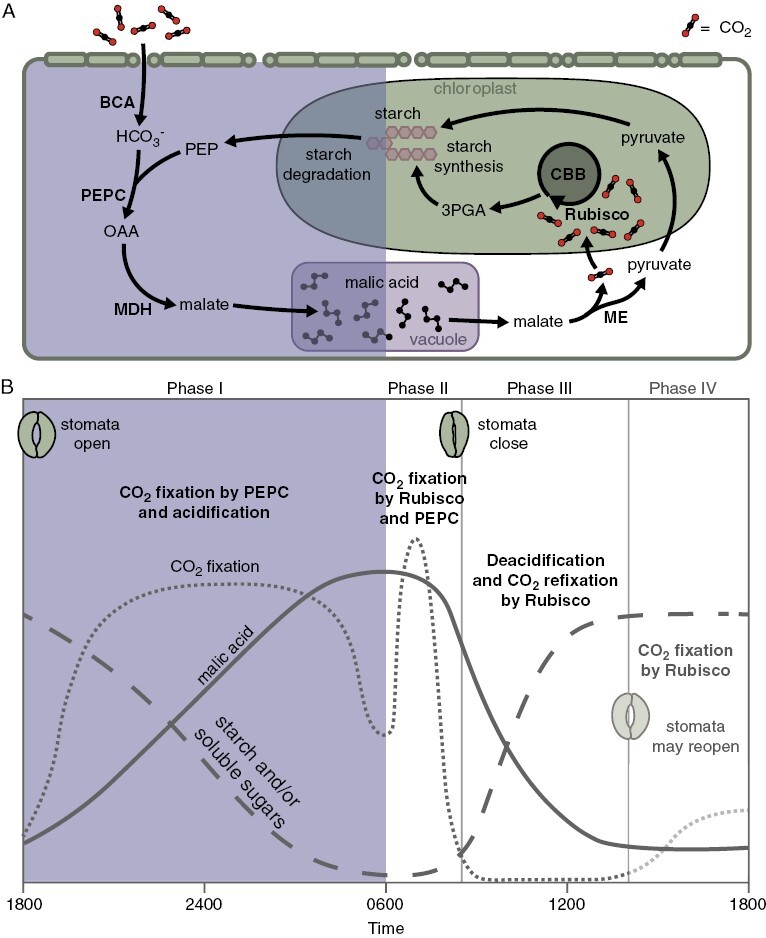
Simplified overview of biochemistry (A) and four phases of CAM (B); phases in (B) are adapted from Osmond (1978). During phase I of CAM, atmospheric CO2 is captured in a series of steps involving phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) carboxylase (PEPC) to form malate, which is stored as malic acid in the vacuole overnight. In phase II, stomata remain open, and both Rubisco and PEPC fix atmospheric CO2. Stomatal closure marks the beginning of phase III, in which malate is released from the vacuole and decarboxylated by malic enzyme (NADP- or NAD-ME) as shown (or PEP carboxykinase, not shown), releasing CO2 to be re-fixed by Rubisco. Finally, if phase IV occurs, stomata reopen, and atmospheric CO2 is fixed predominantly by Rubisco. If phase IV does not occur, stomatal opening is delayed until phase I begins again. Abbreviations: 3PGA, 3-phosphoglycerate; BCA, β-carbonic anhydrase; CBB, Calvin–Benson–Bassham cycle; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; OAA, oxaloacetate.
