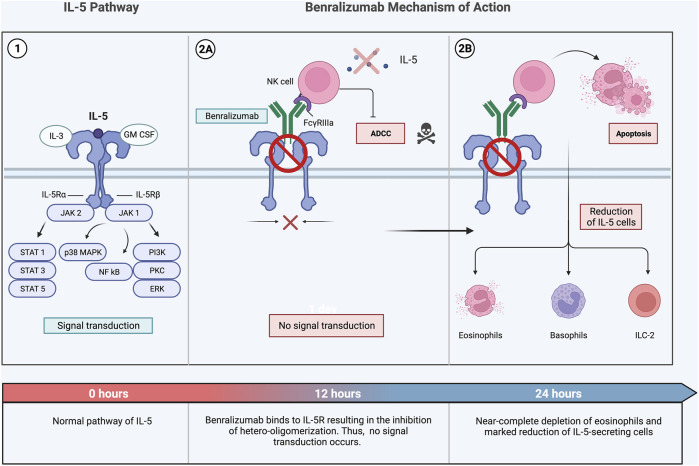
FIGURE 3.
Benralizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets IL-5Rα (1) (Pelaia et al., 2018b). This biological therapy is unique; it is characterized by a dual mechanism of action (2A, 2B). Through interacting with Fab fragments, benralizumab specifically binds IL-5Rα, inhibiting the interaction between IL-5 and its receptor stopping signal transduction on target cells (2A). Additionally, it interacts with the FcγIIIRa receptor expressed by NK cells triggering ADCC-induced apoptosis of eosinophils through the release of pro-apoptotic proteins such as granzymes. (2B) (Pelaia et al., 2018b) Multiple research studies have found a marked depletion in eosinophil, basophils, and proliferation of B-cells in a span of 24 hours following administration of benralizumab (Jackson et al., 2020). Abbreviations: IL-5, interleukin-5; IL-3, interleukin-3; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; JAK, Janus kinase; IL-5Rα, interleukin-5 receptor alpha; IL-5Rβ, interleukin-5 receptor beta; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells; PI3, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; NK cells, natural killer cells; ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.