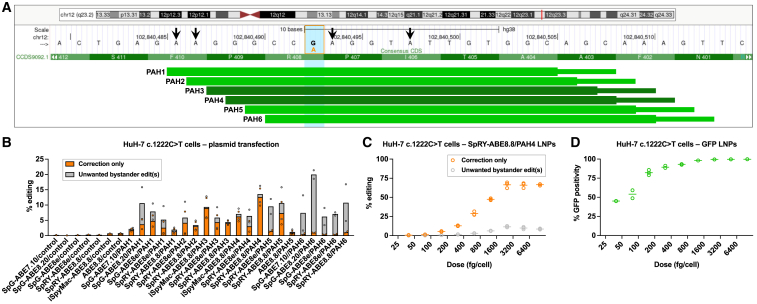
Figure 1.
Base editing to correct PAH c.1222C>T variant in human hepatocytes in vitro
(A) Schematic of the genomic site of the PAH c.1222C>T variant, adapted from the UCSC Genome Browser (GRCh38/hg38). The vertical blue bar outlined by the orange box indicates the G altered to A (in orange) by the variant on the antisense strand. The arrows indicate the sites of potential bystander editing. The horizontal green bars indicate protospacer (thick) and PAM (thin) sequences targeted by the PAH1 through PAH6 gRNAs.
(B) Corrective PAH c.1222C>T editing (determined from genomic DNA) following transfection of cells with plasmids encoding adenine base editor/gRNA combinations (n = 2 biological replicates, one each from two PAH c.1222C>T homozygous HuH-7 cell lines; controls, n = 1), calculated as the proportion of aligned sequencing reads with the indicated type of edits. “Correction only” refers to reads in which the c.1222C>T adenine variant is edited to guanine, with or without base editing of the adjacent synonymous adenine, with no base editing of any other adenines; “unwanted bystander editing” refers to reads in which the c.1222C>T adenine variant is edited to guanine, along with base editing of one or more nonsynonymous adenines.
(C) Dose-response study with PAH c.1222C>T homozygous HuH-7 cells treated with SpRY-ABE8.8/PAH4 LNPs (n = 3 biological replicates).
(D) Dose-response study with PAH c.1222C>T homozygous HuH-7 cells treated with GFP LNPs (n = 2 to 3 biological replicates).